The world was much warmer and greener with meters-higher sea levels just a few thousand years ago.
Between 9000 to 6000 years ago, when global temperatures were 4-6°C warmer than they are today, the Sahara was a tree- and lake-covered haven teeming with megafauna and human civilizations (Manning and Timpson, 2014).

Image Source: LiveScience
During this same period, the Earth’s sea levels were also multiple meters higher than they are now, as there was much less water locked up on land in the form of ice.
In the Persian Gulf region, for example, the biblically-mentioned city of Ur was once located on the sea coast.
Today, Ur’s ruins are located about 200 kilometers inland.
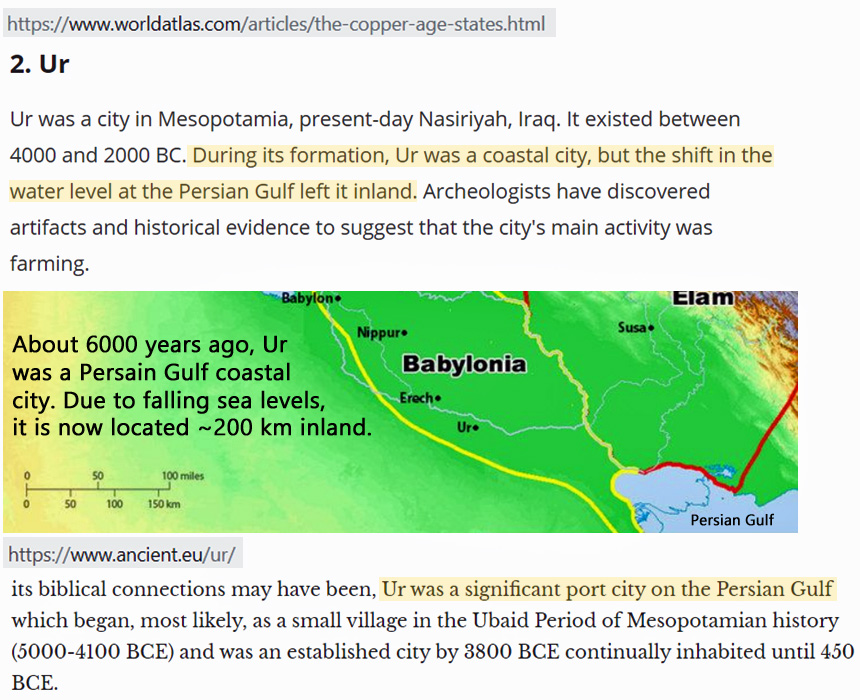
Image Source: WorldAtlas.com and ancient.eu
Scientists have determined the local sea levels were about 2 to 3 meters higher than they are today during that time.






This was after the initial inundation or flood mentioned in Biblical, Mesopotamian, and other World writings.
Same with the ancient city of Troy. The ruins now sits inland whereas when it was at its height the sea was outside its walls.
Portus and Ostia (Antica), harbours of Ancient Rome, are now located a 2 – 3km inland due to silting of the Tiber — or so the Roman Warming Period deniers claim.
[…] Read more at No Tricks Zone […]
Some of that 200 km is probably due to silt carried down by the two rivers, but there seems evidence that the ocean levels dropped 2-3 mm. after Roman times.
Pevensey Castle in the south of England first buildings in Roman times, silting and land reclamation in the Pevensey Levels have pushed the coastline out by about 1.5 kilometres (0.9 mi), leaving the castle landlocked.
> evidence that the ocean levels dropped 2-3 mm. after Roman times.
I assume you meant to say “m.”
There were forests on South American mountains that are being uncovered in the recent warming. Kinda makes on wonder about claims all that warming was local. (And how does one have a “local” sea level rise of a couple meters, anyway?)
Yes, metres.
And not just South America, the Aletsch glacier in eastern Switzerland retreated a few years ago and exposed wood from a forest covered in 1240 A.D. It still hasn’t uncovered a channel in the rock that it moved over 1205 A.D.
Pierre: if you have time try https://kenskingdom.wordpress.com
He is running a series on (South) Australian weather stations, and some innovations e.g. an incinerator near the temperature recorder. Covering also on JoNova.
Thanks to Richard and Chris Hanley for the new info, and to Graeme No.3 for jogging my memory.
Bonjour,
Je ne comprend pas !! comment le doggerland qui sont des terres immergés de la mer du nord a 20 mètres de profondeur pouvaient être au dessus du niveau de la mer du nord il y a 8000/10000 ans,alors que le niveau de la mer était plus élevé de 2 a 3 mètres il y a 9000 a 6000 ans ?
Pour info je suis climatoseptique, mais la je comprend pas ???
Philippe
Can someone translate for Philippe please?
https://notrickszone.com/2017/09/07/past-sea-levels-rose-4-6-meters-per-century-shorelines-retreated-40-meters-per-year-without-co2-flux/
Rapid sea level rise happened once warming started about 10500 years ago. Ice was melted by the warmer climate and the sea level reached a maximum about 6000 years ago. Since then it has moved up and down slightly. Currently it is about 2 metres lower than in Roman times. Thermopolae was a narrow pass between the mountains and the sea in ancient Greece but now is about 10 kilometres wide as the sea level has fallen.
Doggerland was slowly submerged, but the last 15 metres was due to tectonic submersion. As parts of Europe rose after the ice sheet melted (as is still happening in Scotland and Sweden) it acted as a sort of lever causing Doggerland to sink.
[…] https://notrickszone.com/2019/08/01/biblical-city-ur-used-to-sit-on-the-persian-gulf-coast-6000-year… […]
[…] Biblical City Ur Used To Sit On The Persian Gulf Coast 6000 Years Ago. Today Its Ruins Sit 200 km In… […]
[…] https://notrickszone.com/2019/08/01/biblical-city-ur-used-to-sit-on-the-persian-gulf-coast-6000-year… […]
Bonjour et merci,
Dans l’article et les reportage que j’aie lu, a aucun moment il ne parlait de la tectonique des plaques et
du soulèvement provoqué par la fonte de inlandsis Européen d’où ma question !!
Néanmoins il semblerait que ce qui restait du Doggerland il y a 8200 ans a été balayé par un glissement
de terrain de Storegga : https://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glissements_de_terrain_de_Storegga
Merci
Philippe
Hello and thank you,
In the article and the reports that I read, at no point did he talk about plate tectonics and
the uprising caused by the melting of European ice sheets, hence my question !!
Nevertheless it seems that what was left of the Doggerland 8200 years ago was swept away by a slip
Storegga field map: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Storegga_Ground_Lands
Thank you
Philippe
[…] https://notrickszone.com/2019/08/01/biblical-city-ur-used-to-sit-on-the-persian-gulf-coast-6000-year… […]