“The current eager acceptance of oceanic thermal lag as the ‘explanation’ as to why CO2 warming remains undetected, reemphasizes that the atmosphere cannot warm until the oceans do. The logical implication follows that most current climate models are lacking in relevance; they have not been constructed with ocean surface temperature as the fundamental variable. When the problem is attacked from this view, sensitivity to CO2 is significantly reduced; a position also strongly supported by the available palaeoclimatic data.” — Ellsaesser, 1984

According to the IPCC (2013), 93% of the heat energy change from global warming can be found in the oceans (AR5, Chapter 3). Only a tiny fraction of climate change can be accounted for in the atmospheric record, as the heat capacity of the oceans is more than a thousand times greater than the heat capacity of the air. In other words, the widely-publicized surface air temperature change of about +0.6° to +1.0°C since the 19th century is not the main barometer of whether or not global warming has occurred – – and if it has, by how much. Global warming (or cooling) is primarily accounted for as a change in ocean heat content, not surface air temperatures.
Climate models that prognosticate what the temperature of the global climate system might be 100+ years from now, or when atmospheric CO2 concentrations reach 560 ppm (doubled pre-industrial levels) are fundamentally flawed, for they presume that CO2 concentration rise (or decline) is a primary determinant of changes in atmospheric temperature change. It is not. Because of the magnitude of difference in heat capacity, it is the global ocean that determines the temperature of the air (predominantly), not the other way around.
It therefore needs to be established that (1) CO2 variations and ocean heat content changes are correlated (when CO2 falls, ocean heat/temperatures fall, and vice versa); and if they are correlated, then it still needs to be scientifically established (i.e., via experimental observation and measurement) that (2) ocean heat/temperature changes are primarily caused by CO2 variations. Just because there is a correlation between two variables does not necessarily mean that one variable is the cause of the other.
So, as mentioned, first we need to establish a correlation before we can even consider causation. And when it comes to a correlation between CO2 variations and ocean heat content variations, we don’t have one. According to scientific studies of long-term ocean heat content, for 99.975% of the last 10,000 years, there has effectively been no significant correlation between rising or falling CO2 concentrations and rising or falling ocean heat. As will be clarified below, the only period in the last 10,000 years in which CO2 and ocean heat/temperatures sharply rose or fell in concert was the period between 1975 and 2000.
Just 0.09°C – 0.18°C Of Net Warming In 0-2000 m To 0-700 m Ocean Since 1955
Levitus et al. (2012) estimate that, between 1955 and 2010, the global ocean heat energy change (converted to temperature) amounted to an addition of a blistering +0.18°C in the 0-700 m layer, and +0.09°C in the upper 2000 meters of the ocean. That’s less than one-tenth of one degree over 55 years in the 0-2000 m layer.
“The World Ocean accounts for approximately 93% of the warming of the earth system that has occurred since 1955. … The heat content of the World Ocean for the 0–2000 m layer increased by 24.0 ± 1.9 × 1022 J (±2S.E.) [over 1955-2010] corresponding to a rate of 0.39 W m−2 (per unit area of the World Ocean) and a volume mean warming of 0.09°C. … The heat content of the World Ocean for the 0–700 m layer increased by 16.7 ± 1.6 × 1022 J corresponding to a rate of 0.27 W m−2(per unit area of the World Ocean) and a volume mean warming of 0.18°C.”
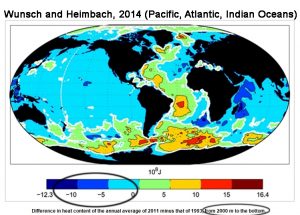
Below the 2000 m depth (and 52% of the ocean waters reside below 2000 m), the “entirety” of the Pacific and Indian Oceans as well as the Eastern Atlantic have been cooling for the last few decades, largely off-setting the already modest change in the 0-2000 m layer.
“Over the 20 yr of the present ECCO state estimate, changes in the deep ocean on multiyear time scales are dominated by the western Atlantic basin and Southern Oceans. … In those same regions, a longer-term general warming pattern occurs below 2000 m. A very weak long-term cooling is seen over the bulk of the rest of the ocean below that depth, including the entirety of the Pacific and Indian Oceans, along with the eastern Atlantic basin.”
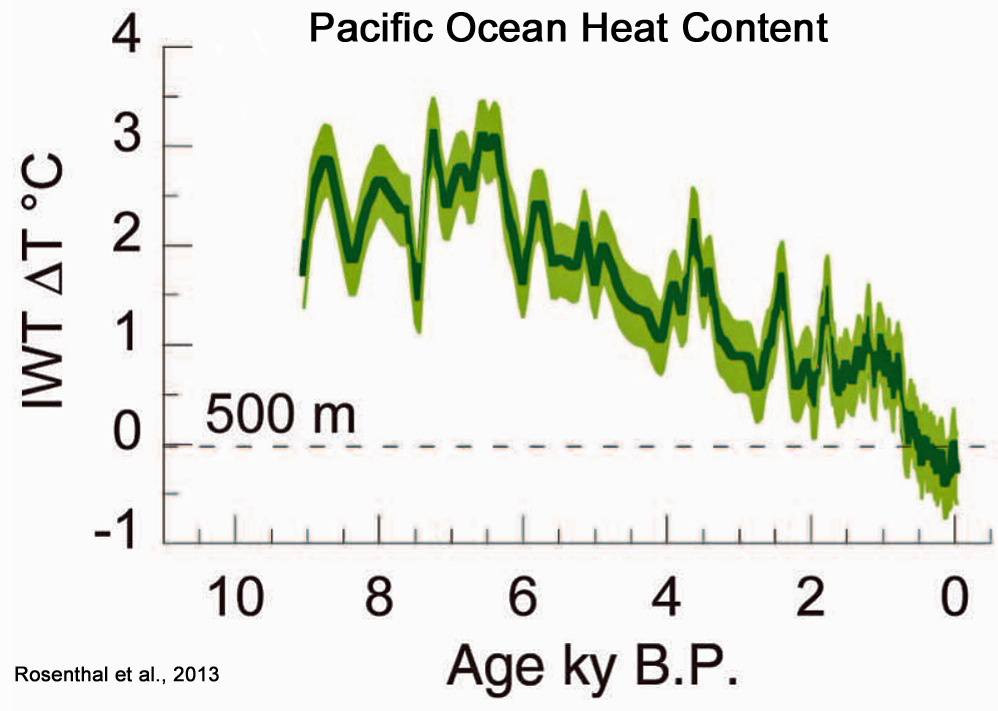
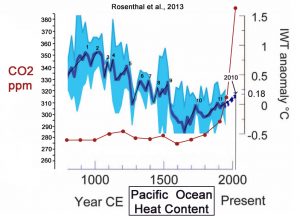
But let’s consider the contextual magnitude of the 0.18°C of warming in the 0-700 m layer since 1955. Below is a graph taken from the Rosenthal et al. (2013) paper published in the journal Science documenting the changes in 0-700 m Pacific Ocean heat content during the Holocene. Pictured are the last 1,200 years (800 C.E. to 2010) of ocean heat changes, including the added blue dotted line on the right extending from 1955 to 2010 (+0.18°C).
As indicated by the black trend bars, notice (a) the amplitude of the rise for the 1900-2010 period is not as steep as 11 previous decadal- and centennial-scale demarcated warming periods during the last 1,200 years. Also notice that (b) the overall sharp drop in ocean heat since the Medieval Warm Period ended (encompassing the 1200 C.E. to 1900 Little Ice Age) was not accompanied by a sharp decline in CO2 concentrations, and that the Medieval Warm Period had flat, not rising, CO2 levels, indicating that CO2 variations could not have been a causal factor in the ocean heat content changes during this entire period (800 C.E. to 1900). Finally, notice that (c) modern temperatures are still tenths of a degree cooler than they were during the 1300 to 1500 C.E. period, when CO2 concentrations still hovered around 280 ppm. In sum, the data in this graph indicate that there has been no significant correlation between CO2 and ocean heat temperature variations for nearly all of the last 1,200 years.
Non-Correlation Between Human CO2 Emissions & Ocean Heat For Most Of The 1900-2010 Period
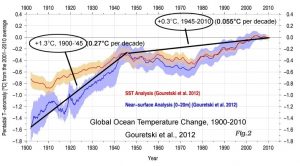
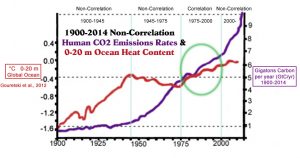
And yes, the non-correlation includes the 1900-2010 period. There are very few reconstructions of global-scale ocean heat content prior to 1950 available in the scientific literature. However, in a paper entitled “Consistent near surface ocean warming since 1900,” Gouretski et al. (2012) provide a comprehensive look at available evidence for the near-surface (0-20 m) change in ocean heat content for the early 20th century. The supplemental graph below (using the available link [red] from the University of Hamburg) was made available upon the release of the paper.
http://icdc.cen.uni-hamburg.de/uploads/pics/hc_fig2.jpeg
Taking a closer look, the graph shows that the amplitude (+1.3°C) and rate (+0.27°C per decade) of the 1900-1945 ocean warming period was about 4 to 5 times as large as the 1945-2010 warming period (+0.3°C, +0.055°C per decade).
In the paper, Gouretski and co-authors point out that the twenty-first century has experienced a general cooling in large regions of the global ocean — just as anthropogenic CO2 emissions (and atmospheric CO2 concentrations) were rising most dramatically.
“[T]he first decade of the 21st century (2001–2010) was not uniformly warmer than previous decades. Before about 1920, the global ocean was almost everywhere colder than the reference decade of 2001–2010. After 1920, several regions of the global ocean were warmer than the reference decade [2001-2010]. … [A] rather abrupt cooling since the end of 1990s both in the East Pacific (connected to the weakening of El Nino and the shift to the negative phase of the Pacific Decadal Oscillation) and in the Southern Ocean may have contributed to a flattening of the global temperature anomaly series after about 2000. …Decadal mean SST and 0–20 m layer anomalies calculated relative to the reference decade 2001–2010 give evidence of the general warming of the global ocean since 1900. However, large regions of the oceans have experienced cooling since the 1990s. Whereas cooling in the tropical Eastern Pacific ocean is associated with frequent La Nina events in the past decade, the cause of the cooling within the Southern Ocean remains unknown.”
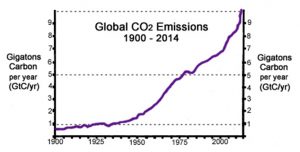
The much larger amplitude and rate of warming that occurred in the early 20th century was not accompanied by a commensurate large change (increase) in anthropogenic CO2 emissions. In fact, throughout the entire 1900 to 1945 period, human emissions only averaged about 1 gigaton of carbon per year (GtC/yr). In contrast, human emissions rates rose sharply to 4 GtC/yr by the 1970s, 6 GtC/yr by the 1990s, and over 10 GtC/yr by 2014. Atmospheric CO2 followed a similar trajectory, as concentrations rose by just 15 ppm in the 40 years between 1900 and 1950 (295 ppm to 310 ppm), whereas concentrations rose by 85 ppm in the 65 years after 1950, including 22 ppm just between the years 2000 and 2010 alone (Feldman et al., 2015) — a decade when near-surface ocean heat “flattened” according to Gouretski et al. (2012). And despite this explosive increase in human CO2 emissions and atmospheric CO2, the near surface ocean heat content actually cooled between 1945 and 1975, and the rate of warming since 1975 has been much less pronounced than during the 1900-1945 period.
If we were to visually combine the record of the explosive rise in human CO2 emissions since 1945 with the record of near-surface ocean heat content for the entire 1900-2010 period, it would be evident that the only decadal-scale period in which CO2 emissions steeply rose in concert with ocean temperature was during the 25 years between 1975 to 2000. For 1900-1975 and 2000-2010, there was no obvious correlation between rapidly rising CO2 and ocean heat content.
No Correlation Between CO2 Variations And Ocean Heat For The Entire Holocene
And not only is there a lack of correlation between rising CO2 and rising ocean heat content for all but the 1975-2000 period during the years 800 C.E. through 2010, there is also no correlation between rising CO2 and rising ocean heat for the entirety of the Holocene. Actually, the general long-term trend is for there to be an inverse correlation: as CO2 rises, ocean heat content declines. The following Rosenthal et al. (2013) graph of the Pacific Ocean’s 0-500 m layer demonstrates this.

Conclusion
To summarize, in the last 10,000 years, there was one 25-year period (1975-2000) in which CO2 levels and ocean heat content rose in concert. Other than that, the rest of the last 10,000 years contained no obvious correlation between ocean heat content variations and the rise and fall of CO2 concentrations. Without a significant long-term (or short-term) correlation between these two variables, we cannot even begin to address the causality question.
Simply put, the presumption that variations in CO2 concentrations cause global warming — net increases in global-scale ocean heat content — has not been established.





Well put and that is exactly the point.
On a planet were the majority of the surface is water, where most of the atmosphere is damp, water and its temperature variations are the major league play in what happens climatically.
CO2 is less than a bit part player.
“Simply put, the presumption that variations in CO2 concentrations cause global warming — net increases in global-scale ocean heat content — has not been established.”
Do you think CO2 doesn’t absorb any infrared energy, or do you think the Earth doesn’t emit any?
“Do you think CO2 doesn’t absorb any infrared energy, or do you think the Earth doesn’t emit any?”
According to modeling, yes, CO2 absorbs infrared. But as even RealClimate acknowledges, cloud radiative forcing is immensely more influential in determining the energy budget than is CO2 :
RealClimate: “Of course the range of net infrared forcing caused by changing cloud conditions (~100W/m2) is much greater than that caused by increasing levels of greenhouse gases (e.g. doubling pre-industrial CO2 levels will increase the net forcing by ~4W/m2)”
Ramanathan et al., 1989: “The size of the observed net cloud forcing is about four times as large as the expected value of radiative forcing from a doubling of CO2. The shortwave and longwave components of cloud forcing are about ten times as large as those for a CO2 doubling.”
Can you explain why it is that there has been no correlation between CO2 changes and OHC changes for nearly all of the entire Holocene, or why the oceans are still about 0.65 C colder than they were 1,000 years ago, when CO2 levels were 125 ppm lower than now?
Can you explain why it is that OHC plummeted between the Medieval Warm Period and Little Ice Age — while CO2 levels were slightly rising? Since CO2 variations didn’t cause that dramatic change in OHC, what *was* the physical mechanism causing that dramatic change? Solar activity?
Can you explain why it is you are a believer in causation (CO2 –> OHC) when a *correlation* between those two variables has not even been established?
Finally, answer this question, David, using results (physical measurements) from a scientific experiment.
If the CO2 concentration above a body of water was lowered by -10 parts per million, what would the heat change (convert to temperature) be for the first 1 meter? Again, cite the results of an observational experiment (not a theoretical model) that has actual physical measurements for the observed change in water heat directly due to CO2 concentration variations.
Let’s see how many of these questions you answer.
Kenneth Richard says:
“According to modeling, yes, CO2 absorbs infrared.”
Kenneth, learn.
The absorption properties of CO2 were established experimentally by Tyndall in 1861.
“On the Absorption and radiation of Heat by Gases and Vapours, and on the Physical Connexion of Radiation, Absorption, and Conduction,” John Tyndall, Philosophical Magazine Series 4, 22, 169-194, 273-285 (1861).
http://www.gps.caltech.edu/~vijay/Papers/Spectroscopy/tyndall-1861.pdf
and in 1856 by American Eunice Foote. See
http://www.davidappell.com/EarlyClimateScience.html
There has been no scientific or physical experiment that demonstrates that raising or lowering CO2 concentrations in volumes of 0.000001 (1 part per million) are correlated, let alone cause variations in OCEAN HEAT CONTENT, where 93% of the heat energy from “global warming” is claimed by the IPCC to end up. The air doesn’t warm or cool unless the oceans do — because of the immense heat storage capacity difference between the air and water. Again, we have no physical measurements or observations demonstrating that atmospheric CO2 heats water. You are once again relying on 160-year-old models that are based on high school science lab observations, not real world data. Even SkepticalScience and RealClimate.org acknowledge that the presupposition that CO2 heats water has not been physically tested, let alone observed. Cloud variations have to be used as proxy.
SkS: “Obviously, it’s not possible to manipulate the concentration of CO2 in the air to carry out real world experiments, but natural changes in cloud cover provide an opportunity to test the principle [that CO2 heats water].”
RC: “Clearly it is not possible to alter the concentration of greenhouse gases in a controlled experiment at sea to study the response of the [ocean] skin-layer. Instead we use the natural variations in clouds to modulate the incident infrared radiation at the sea surface.”
In other words, your presuppositions are based on models, not actual physical measurements or experimental observations. Science without observational evidence is not science. I challenged you to cite observational evidence that CO2 heats water. You’ve once again demonstrated that you cannot — which isn’t the least bit surprising since that evidence doesn’t exist.
And perhaps, David, you could find some scientific papers that are a bit more modern:
Ellis and Palmer, 2016
Conclusion: [I]nterglacial warming is eccentricity and polar ice regrowth regulated, Great Summer forced, and dust-ice albedo amplified. And the greenhouse-gas attributes of CO2 play little or no part in this complex feedback system.
Hertzberg and Schreuder, 2016
Nothing in the data supports the supposition that atmospheric CO2 is a driver of weather or climate, or that human emissions control atmospheric CO2.
Vares and Persinger, 2015
Earth’s Diminishing Magnetic Dipole Moment is Driving Global Carbon Dioxide Levels and Global Warming
Introduction: The consensus of opinion regarding the increases in global temperature as causally connected to anthropogenic sources of CO2 is primarily based upon models rather than quantitative or multivariate analyses of actual data.
Smithuesen et al., 2015
Abstract: For this region [central Antarctica], the emission to space is higher than the surface emission; and the greenhouse effect of CO2 is around zero or even negative, which has not been discussed so far. We investigated this in detail and show that for central Antarctica an increase in CO2 concentration leads to an increased long-wave energy loss to space, which cools the Earth-atmosphere system. … For most of the Antarctic Plateau, GHE-TES [greenhouse effect as measured by the Tropospheric Emission Spectrometer] is close to zero or even slightly negative; i.e., the presence of CO2 increases radiative cooling
Garfinkel et al., 2015
[A] large fraction of the recently observed changes [sea surface temperatures, ozone] may, in fact, be a consequence of natural variability and not a response of the climate system to anthropogenic forcings.
Avakyan, 2013
The contribution of the greenhouse effect of carbon-containing gases to global warming turns out to be insignificant.
Florides and Christodoulides, 2009
A very recent development on the greenhouse phenomenon is a validated adiabatic model, based on laws of physics, forecasting a maximum temperature-increase of 0.01–0.03 °C for a value doubling the present concentration of atmospheric CO2.
Chilingar et al., 2009
[A]ccumulation of small additional amounts of carbon dioxide and methane in the atmosphere as a result of anthropogenic activities has practically no effect on the Earth’s climate.
Do you think the models say anything relavent to this world because I do not.
CO2 does NOT generate heat you advocate. Nor can it hold heat! It is just a gas, at really very, very, very miniscule part of our atmosphere at about 400 part per million.
Dr. Habibullo Abdussamatov has a better idea of climate and its trend than anything the AGW advocates (including you David Appell) came out with.
Dr. Habibullo Abdussamatov is a real scientist doing real science unlike the vast majority of NASA, GISS, Hadley virtual ‘climate scientist™’ know nothings.
So not to put too fine a point on it Appell you should go and read some of his real science and give up on the advocacy.
tom0mason says:
“CO2 does NOT generate heat you advocate.”
Of course it doesn’t.
Go learn some science in order to stop saying foolish things like this.
The only fooling things said around here are by you,
Stick to sci-fantasy writing… its all you have,.
I have learned more science than you’ll ever understand. And the one thing I fully understand, and you are yet to learn, is ‘science’ per se is not a fixed point. Be aware that your confident protestations might become the source of your future embarrassment if you were ever to become fully conscious of the world about you and realize that right now you do not know enough.
So tell us how clouds work, I’m sure you must know, given you much trumpeted ‘science’ background you’ll have no problem giving references to modern observational measurements (of dynamic changes in radiations, energy balance, temperature and chemistry, etc.), and of why a cloud forms where it does, how it progresses and its ultimate destiny.
Or maybe you are able to explain why and how, given your version of ‘science’, does the Antarctic cool more as CO2 levels increase (as has been observed).
Or can you only pontificate endlessly about a modeled world, and not a scientifically observed, measured real world.
David Appell hasn’t a clue.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Y2K1uHvfaek
water vapor gives negative, not positive feedback.
“Do you think CO2 doesn’t absorb any infrared energy, or do you think the Earth doesn’t emit any?
OMG, rotten. Basic physics.
Now PROVE that it causes warming in a convection controlled atmosphere. (especially when it doesn’t re-emit below 11km. https://s19.postimg.org/s6jyed10z/stratospheric_cooling.jpg)
You have NO PROOF, and YOU KNOW IT !!
Just like you have NO PROOF that birds are killed by coal fired power stations.
There is NO WARMING in the satellite temperature series apart from El Nino and ocean effects.
No CO2 signature what so ever…. END OF STORY !!
For David to “prove” that CO2 variations cause atmospheric warming/cooling, he’d have to first “prove” that CO2 variations cause abyssal ocean warming/cooling, since the atmospheric temperatures respond to ocean heat changes, not the other way around.
David, please provide scientific proof that atmospheric CO2 concentration changes in volumes of 0.000001 (1 ppm) are *the* cause of changes in ocean heat energy, superseding the heating influence of Sun and cloud cover variations. Provide physical measurements from scientific experiments, and include citations.
David rotten has NEVER been able to prove anything.
He is a low-end sci-fantasy writer for a back-water rag… That is all he is and all he ever will be.
“Radiative forcing – measured at Earth’s surface – corroborate the increasing greenhouse effect,” R. Philipona et al, Geo Res Letters, v31 L03202 (2004)
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1029/2003GL018765/abstract
“Observational determination of surface radiative forcing by CO2 from 2000 to 2010,” D. R. Feldman et al, Nature 519, 339–343 (19 March 2015)
http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v519/n7543/full/nature14240.html
Press release for Feldman et al: “First Direct Observation of Carbon Dioxide’s Increasing Greenhouse Effect at the Earth’s Surface,” Berkeley Lab, 2/25/15
http://newscenter.lbl.gov/2015/02/25/co2-greenhouse-effect-increase/
Poor David.
Still cannot come to grips with the FACT that the ONLY warming in the whole satellite period has come from NON-CO2 El Nino and ocean cycle affects.
That is the empirical evidence that he continues to ignore.
The Earth’s atmosphere is controlled by the thermos gravity effect, and there is NOTHING you can do about it.
Have you seen the massive cold cell now forming over Europe as the last of the heat from the EL Nino and north Atlantic blog gets sucked away up into the Arctic.
Going to be pretty funny watching you and your fellow cultists over the next few years as temperatures start to drop. 🙂
Philipona’s paper..in the abstract….
“Model calculations show the…. “… OOPS !!!
I stopped reading.
—————————
As for the Feldman studies.. ROFLMAO !!
The authors started in the 2000 La Nina, and ended at the 2010 El Nino – when troposphere temperatures were half a degree warmer. Then they noticed that there was slightly more downwelling longwave radiation, which they blamed on increased absorption from the increase in CO2. DOH !!!
https://stevengoddard.files.wordpress.com/2015/02/screenhunter_7435-feb-26-00-15.gif
The increase in DLWR was due to the warmer troposphere during the El Nino. Warmer air emits more longwave radiation. The higher concentration of CO2 will also emit more DLWR radiation, but that is not due to increased absorption.
So ..Purely a case of wishful thinking or monumental cherry-picking of their data.
I wonder how much they would have noticed if they had stopped at 2008, or continued to 2011.
Maybe their data did go further…… 5 years between end of data and publishing seems a long time in the publish or perish world of climate science fantasy.
oh dear.. even worse..
“The spectrum it sees looks very much like the one we’d calculated it should see, with a few exceptions caused by heating of the instrument itself. But the precise details vary based on the factors noted above, like the weather and seasons. Using a decade-long time series, the authors are able to get all these other factors to effectively cancel out; what emerges shows “the unmistakable spectral fingerprint of CO2.”
So they never really detected it, but after adjustments they were allowed to keep their jobs.
Confirmational bias written all over it.
Further
”Similar to the clear-sky study, we also provide the all-sky upwelling SW and LW fluxes to study the surface radiation budget under all-sky conditions. The rates of net SW and LW fluxes are −0.07 W/m^2 [per year] and −0.37 W/m^2 [per year], respectively, resulting in a DECREASE of 0.44 W/m^2 per year in NET flux at the surface (Figure 3b). The decline of NET flux, however, does not correlate with the increased surface air temperature as illustrated in Figure 3a. The surface air temperature is determined by the sum of NET radiation fluxes (downwelling and upwelling SW and LW fluxes) and nonradiative fluxes (sensible and latent heat fluxes, ground heat flux and energy flux used for melt), as well as the large-scale advection [Wild et al., 2004]. Wild et al. [2004] investigated this counterintuitive result and concluded that it may be due to a decrease of surface evaporation and associated reduced evaporative surface cooling.”
”… using the Stefan-Boltzmann equation indicates that an annual increase of 0.04°C air temperature each year corresponds to an increase of 0.4 W/m^2 per year in upward LW upward surface emission. However, the measured change is a DECREASE of 0.26 W/m^2 per year as shown in Figure 2e.”
Dong, Xiquan, Baike Xi, and Patrick Minnis 2006. “Observational evidence of changes in water vapor, clouds, and radiation at the ARM SGP site.” Geophysical Research Letters
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1029/2006GL027132/full
And a bit more fun with this Marty Feldman paper..
https://tallbloke.wordpress.com/2015/02/26/new-result-shows-co2-has-almost-no-effect-on-temperature/
Then of course there is the FACT that the Antarctic just measured 400ppm a little while ago..
but there is NO WARMING AT ALL over the last 38 or so years.
https://s19.postimg.org/5dm8qkc4z/UAH_So_Pol_All.png
As usual, you have NOTHING but PROPAGANDA BS.
and are unable to back up anything you say with real science.
According to Feldman et al., 2015, the radiative effect for the +22 ppm increase in atmospheric CO2 between 2000 and 2010 amounted to a paltry 0.2 W m-2 per decade. In contrast, surface solar radiation and shortwave cloud forcing since the 1980s accounts for between 1.0 and 4.0 W m-2 per decade on a net global scale. Which RF value do you think is larger: 0.2 W m-2 for CO2, or ~2.5 W m-2 for SSR/clouds? In case you missed this, the negligible effect of CO2 forcing relative to SSR/cloud forcing is explained here:
https://notrickszone.com/2016/10/27/3-new-papers-reveal-dominance-of-solar-cloud-forcing-since-the-1980s-with-co2-only-a-bit-player/
In addition, were you aware that Feldman et al., 2015 is entirely contradicted by Song, Wang, and Tang, 2016, as the latter scientists have determined the radiative forcing associated with the 1992-2014 period amounted to -0.04 W m-2, not the 0.2 W m-2 per decade found in Feldman et al., 2015? In other words, the dramatic increase in CO2 emissions rates since 1992 (from 6.1 GtC/yr to 10.1 GtC/yr) has resulted in no net radiative influence on the overall greenhouse effect. The link from a few weeks ago explains this:
https://notrickszone.com/2016/09/19/new-paper-documents-imperceptible-co2-influence-on-the-greenhouse-effect-since-1992/
Song, Wang, and Tang, 2016
[T]he primary goal of this study is to investigate the spatiotemporal evolution of the greenhouse effect to better evaluate its potential impact. … Because of the shorter period of the CERES EBAF product, the areal averaged Gsa [surface greenhouse effect] is represented only between 2003 and 2014 in Fig. 2 but shows no notable trend over the globe, sea or land. Thus, the surface greenhouse effect has not been strengthened in the last decade.
In the 1980s, a significant increasing Gaa [atmospheric greenhouse effect] tendency exists with a linear estimate of 0.19 W m−2 yr−1. However, this uprising trend pauses starting in circa 1992, when Gaa [atmospheric greenhouse effect] begins to slightly decrease at a rate of −0.01 W m−2 yr−1. This statistically non-significant trend indicates that the enhancing global atmospheric greenhouse effect is slowed down. Moreover, the atmospheric greenhouse effect hiatus can be found over both sea and land.
The oceanic Gaa [atmospheric greenhouse effect] exhibits a notable increasing trend with a rate of 0.21 W m−2 yr−1 in 1979–1991, whereas its rate of change (−0.04 W m−2 yr−1) during 1992–2014 is not statistically significant.
tom0mason wrote:
“CO2 is less than a bit part player.”
Explain this TOA observed data:
http://www.giss.nasa.gov/research/briefs/schmidt_05/curve_s.gif
David, the “A” in TOA stands for atmosphere. This is an essay about changes in ocean heat, and how variations in CO2 concentrations do not correlate with OHC changes.
So why is it your belief that atmospheric heating and cooling variations are what determine ocean heat variations when the heat capacity of the oceans is more than 1,000 times greater than the heat capacity of the air? Why do you believe that the air has more of a capacity to heat the deep ocean than the other way around?
Kenneth, so you can’t explain that TOA data? It’s crucial to everything else….
David, of course triatomic gases at the top of the atmosphere cool the planet by radiating into space. What’s your point? If there were no triatomic gases in the atmosphere , the surface would radiate directly into space.
Do you not grasp this?
There is only one little thing DA every grasps. !!
“Kenneth, so you can’t explain that TOA data?”
Again, David, 93% of the heat change from “global warming” is found in the oceans. The top of the atmosphere doesn’t heat the oceans; the oceans heat the atmosphere, as the heat capacity of oceans is 1,000+ times greater than the heat capacity of the air.
There has been no scientific experiment or observational evidence that shows CO2 concentration variations in volumes of + or – 0.000001 heat or cool water. If you think there is, please cite the physical measurements.
And please explain why you think it is that CO2 concentrations and ocean heat content variations do not even correlate with one another. What caused OHC to plummet during the Little Ice Age, David? CO2 levels rose (slightly) during that period. So what was the physical mechanism causing the cooling? Answer this question, please.
Only in the unreal modeled world that you appear to reside in.
CO2 is less than a bit player as so many studies have shown.
See above and so many other post here for the real world evidence.
What you have linked to David, is a graph showing that CO2 aborbs and emits IR strongly at 15 µm.
Accoring to Wien’s Displacement Law, 15µm radiation has a corresponding temperarture of -80ºC.
The entire toposphere has a temperature above -80ºC. That is why CO2 has no effect on tropospheric temperature, let alone ocean temperatures.
Cheers
Will
Will, you have very much misunderstood the meaning of Wien’s Law.
How the heck would a Low-end fantasy writer like you have any idea if someone had misunderstood anything to do with science
You are FOOLING only yourself, appell-grub.
Well of course you would say that wouldn’t you David.
But let’s just concentrait on a couple of aspects here. CO2’s ability to warm the atmosphere entirely depends on it’s specific temperature, nothing else.
If CO2 is radiating 15µm radiation, according to Wien’s diplacement law, the temperature of a subtance radiating 15µm radiation will be -80ºC.
Any subtance which emits IR does so in accordnce to it’s specific temperature. That tempreature has a corresponding wavelength, as per Wien’s displacement law.
Will Pratt says:
“But let’s just concentrait on a couple of aspects here. CO2’s ability to warm the atmosphere entirely depends on it’s specific temperature, nothing else.”
Totally wrong.
CO2 absorbs upwelling IR from the Earth. It then re-emits it in a random direction; half of those re-emissions have a downward component. THAT’S global warming.
“CO2 absorbs upwelling IR from the Earth. It then re-emits it in a random direction; half of those re-emissions have a downward component. THAT’S global warming.”
According to the IPCC, 93% of “global warming” occurs via changes in ocean heat content. Since even RealClimate.org and SkepticalScience acknowledge that ocean heat content changes are far more influenced by variations in cloud cover than by changes in CO2, explain why it is your belief that CO2 is nonetheless the primary cause of ocean heat content changes.
RC: “Of course the range of net infrared forcing caused by changing cloud conditions (~100W/m2) is much greater than that caused by increasing levels of greenhouse gases (e.g. doubling pre-industrial CO2 levels will increase the net forcing by ~4W/m2)”
No David, IR is not heat and that is the point I made above. It doesn’t matter how much IR is radiated back down. If it doesn’t have sufficient flux to heat the molecules below, and it doesn’t, no warming occurs. This is simple thermodynamics, come on man it’s not that hard to grasp.
IR emissions from CO2 @ 15µm cannot heat any molecules in the troposphere because the peak of that 15µm radiation is the equals -80ºC. That is a law of physics and it cannot be argued with.
No David, IR is not heat and that is the point I made above. It doesn’t matter how much IR is radiated back down. If it doesn’t have sufficient flux to heat the molecules below, and it doesn’t, no warming occurs. This is simple thermodynamics, come on man it’s not that hard to grasp.
IR emissions from CO2 @ 15µm cannot heat any molecules in the troposphere because the peak of that 15µm radiation is the equals -80ºC. That is a law of physics and it cannot be argued with.
So David, explain Wien’s Law to us. You’re an ex science journalist, I know you can do it. Go for it.
He’s more acquainted with “Whine’s Law,” where the more annoying you make yourself, the more you feel you’ve accomplished.
He is certainly accomplishing making a MOCKERY and a FOOL of himself.
@AndyG55 6. November 2016 at 9:18 PM
He does that well, I’ll give him that. =)
Dirk: Wien’s Law is simple. Go read Wikipedia.
In other words, you Can’t explain it.
Good Lord, can’t you people even read and understand abstracts?
“Parts of the deeper ocean, below 3600 m, show cooling…. In the global average, changes in heat content below 2000 m are roughly 10% of those inferred for the upper ocean over the 20-yr period.”
Wunsch and Heimbach 2014
http://journals.ametsoc.org/doi/full/10.1175/JPO-D-13-096.1
What a load of ABYSSMAL CRAP.
There is basically NO DATA for even the upper ocean before 2003.
This is a NOTHING paper based only on presumption and fantasy garbage.
“dynamically consistent state estimate is used for the period 1992–2011”
WTF !!! GARBAGE… nothing else but GARBAGE.
“Parts of the deeper ocean, below 3600 m, show cooling.”
ROFLMAO.. show us the measurement you brain-washed cretin.
There are NONE… and you KNOW it.
While you are at it, show us the birds killed by coal fired power stations… still waiting.. you LYING POS !!
You are NOTHING by an EMPTY WASTE OF SPACE.
See that little flat bit at the end of the Ocean heat content graph.
That is where they actually started measuring it using ARGO
Anything before that is based on models built on assumptions, and very little data at all.
You can see from this figure that they have basically no coverage below 700m even up until2003, especially in the southern hemisphere.
https://s19.postimg.org/46xcg7377/figure_42.png
Yes, and that’s exactly why Phil Jones himself has said that the data for the ocean has been “made up”.
date: Wed Apr 15 14:29:03 2009
from: Phil Jones subject: Re: Fwd: Re: contribution to RealClimate.org
to: Thomas Crowley
Tom,
The issue Ray alludes to is that in addition to the issue of many more drifters providing measurements over the last 5-10 years, the measurements are coming in from places where we didn’t have much ship data in the past. For much of the SH between 40 and 60S the normals are mostly made up as there is very little ship data there.
Less than 20% of the SH oceans covered before 2003.
Gees, even the surface station data has more coverage than that !! 🙂
The late Dr Robert Stevenson, oceanographer, did a critique of the first Levitas et al paper, 2000, in this article.
“Yes, the Ocean Has Warmed; No, It’s Not “Global Warming” by Dr. Robert E.
Stevenson
http://www.21stcenturysciencetech.com/articles/ocean.html
A few quotes:
“Contrary to recent press reports [2000 and still they pursue it] that the oceans hold the still-undetected global atmospheric warming predicted by climate models, ocean warming occurs in 100-year cycles, independent of both radiative and human influences.”
“The climate models had predicted a global temperature increase of 1.5°C by the year 2000, six times more than that which has taken place.
Not discouraged, the modellers argue that the heat generated by their claimed “greenhouse warming effect” is being stored in the deep oceans, and that it will eventually come back to haunt us. They’ve needed such a boost to prop up the man-induced greenhouse warming theory, but have had no observational evidence to support it. The Levitus, et al. article is now cited as the needed support.”
“Prof. Hubert H. Lamb, the premier European climatologist of the 20th
century, wrote in 1977 that “there has been a general warming of sea
temperatures, by 0.5-1.0°C, from 1880 to 1965, defined from widely scattered
points around the oceans of the world.”
“Surface water samples were taken routinely, however, with buckets from the deck
and the ship’s engine-water intake valve. Most of the thermometers were calibrated into 1/4-degrees Fahrenheit.
I would guess that any bucket-temperature measurement that was closer to the actual temperature by better than 0.5° was an accident, or a good guess.
The archived data used by Levitus, and a plethora of other oceanographers, were taken by me, and a whole cadre of students, post-docs, and seagoing technicians around the world.”
“The atmosphere cannot warm until the underlying surface warms first. The lower
atmosphere is transparent to direct solar radiation, preventing it from being
significantly warmed by sunlight alone. The surface atmosphere thus gets its
warmth in three ways: from direct contact with the oceans; from infrared
radiation off the ocean surface; and, from the removal of latent heat from the
ocean by evaporation. Consequently, the temperature of the lower atmosphere is
largely determined by the temperature of the ocean.
“Because of the high density/specific heat of sea water, the entire heat in
the overlying atmosphere can be contained in the top two meters of the oceans.
This enormous storage capacity enables the oceans to “buffer” any major
deviations in temperature, moderating both heat and cold waves alike.”
“For the past two decades at least, [in 2000] and possibly for the past seven decades, the Earth’s true surface air temperature has likely experienced no net change”
“Climate models that prognosticate what the temperature of the global climate system might be 100+ years from now, or when atmospheric CO2 concentrations reach 560 ppm (doubled pre-industrial levels) are fundamentally flawed, for they presume that CO2 concentration rise (or decline) is a primary determinant of changes in atmospheric temperature change. It is not. Because of the magnitude of difference in heat capacity, it is the global ocean that determines the temperature of the air (predominantly), not the other way around.”
This is a fundamentally misguided understanding of climate models. The only “presumption” that GCMs make about CO2 is that it absorbs at certain wavelengths of light. That’s it. As atmospheric CO2 increases in the model run, the amount of absorption then changes, which ultimately results in both increasing surface temperature AND ocean heat content as total energy in the Earth system rises. They are outcomes from modelling, not assumptions.
Note that your opening quote is about sea surface temperatures, not ocean heat content. It is entirely uncontroversial to say that global warming cannot proceed very far without warming sea surface temperatures – it’s a characteristic of climate model simulations (e.g. https://www.gfdl.noaa.gov/blog_held/11-is-continental-warming-a-slave-to-warming-of-the-ocean-surface/). But of course, sea surface temperatures are also influenced by increased energy budget due to higher CO2 levels. Hence, SSTs have gone up.
The comparison you present relating to Gouretski et al. 2012 is not like-for-like. They present a better comparison in the actual paper, showing an SST average masked to the much smaller and homogeneous coverage of 0-20m observations. It demonstrates that the large early 20th Century trend in the 0-20m curve is not globally representative.
The Rosenthal paper is interesting, but seems to be fairly new in its interpretations and assumptions about how the single-location proxy data relate to wider Pacific and even global trends. Probably shouldn’t place too much weight on it at this point. Even so, the results it presents would not contradict any theory relating to CO2 influence – CO2 variations over the Holocene are small so wouldn’t be expected to override large trends due to other factors.
What we can say with our global array of ocean temperature and sea level observations over the past several decades is that the rise in ocean heat content is very much consistent with expectations from modelling anthropogenic climate influence.
PaulS:
Paul, ostensibly without knowing it, you have succinctly summarized the fundamental flaw in the CO2-causes-global-warming paradigm.
Indeed, “outcomes from modeling” are not rooted in observations — and that is entirely the problem here — and why the word “assumption” is used (appropriately). It is precisely the point that we have no observational evidence (i.e., controlled scientific experiment, physical measurements) that raising or lowering CO2 concentrations in volumes of 0.000001 (ppm) even affect ocean heat content (or sea surface temperatures), let alone predominantly cause changes in deep ocean heat. It’s entirely rooted in presumption to claim that varying CO2 concentrations over a body of water causes heat changes in that body of water. No scientific experiments involving actual CO2 variation and measured water temperature/heat change exist to confirm that rising CO2 “increases the surface temperature AND ocean heat content” as you claim. It’s hypothetical. Actually, since hypotheses have to rely on actual observational evidence, it’s worse than hypothetical. It’s presuppositional and presumptive. Belief.
If you don’t agree, and you do think we have observational evidence that raising or lowering CO2 levels cause changes in deep ocean heat, please cite a scientific experiment and concomitant physical measurements that confirm this. Keep in mind that no less than the RealClimate.org and SkepticalScience blogs acknowledge that we don’t have any scientific experiments or direct observational evidence demonstrating that CO2 increases deep or surface water temperatures.
Essentially all you have done here is declare that since CO2 concentrations have risen since 1955 and deep ocean temperatures have risen (by a sweltering 0.09 C) since 1955 (presuming the Levitus et al. [2012] pre-ARGO 1955-2004 ocean data are correct), therefore CO2 concentrations cause OHC changes. It’s the post hoc fallacy, blaring and hollering: “Since event Y followed event X, event Y must have been caused by event X.”
As the original essay suggests, there was no correlation between the dramatic drop in OHC following the Medieval Warm Period and a change in CO2 concentrations as shown by the Rosenthal et al. (2013) paper. Actually, the two variables are inversely correlated, if there is a correlation at all: OHC declined as CO2 rose throughout the Little Ice Age (as well as the entire Holocene, as shown in the last Rosenthal graph).
The reason why the Gouretski paper was used is because we have next to no information about deep ocean temperatures prior to 1955, and at least the Gouretski paper provides an outline of what the near-surface temps might perhaps have possibly looked like during the 1900-1955 period.
Sheesh, we still don’t even have much of any data on the OHC below 2000 m for the 21st century, let alone the 20th, and the majority of ocean water resides below 2000 m. So the Levitus paper uses an arbitrary cut-off (2000 m) for educated guessing of what OHC might have been since 1955. Simply put, we have almost no information about OHC prior to 1955, and the post-1955 data aren’t conclusive either. The errors and uncertainties are immense. Even sea surface temperatures for the vast majority of the SH were admittedly “made up” by the dataset creators (Phil Jones, Tom Wigley), as we had/have very limited information there.
PaulS:
Again, please provide direct observational evidence (controlled scientific experiment, physical measurements) that higher CO2 levels are the cause of higher sea surface and deep ocean temperatures, and lower CO2 levels are the cause of lower sea surface and deep ocean temperatures. Cite the evidence that CO2 changes cause temperature changes in water. You are assuming cause because we have a few decades of apparent correlation. We have 10,000 years of non-correlation (or inverse correlation). Correlation does not automatically mean causation.
Let’s see your physical data showing CO2 heats ocean water. Models are not physical evidence. Don’t rest on assumption and belief. That’s not science.
“and deep ocean temperatures have risen (by a sweltering 0.09 C) since 1955”
I really want to know how they measured the deep ocean temperatures to two decimal places in 1955 😉
It is nothing but models based on assumptions.
And, of course, as soon as we did start actually measuring it in a consistent way (ARGO) in 2003, the modelled rise has change to a zero rise.
Just wanted to assure you, AndyG55, that I am in full agreement with you regarding the coverage/sampling problem and the fact that it is all little more than modeled guesses prior to ARGO. I only use the stated values by Levitus et al. (2012), Gouretski et al. (2012), Rosenthal et al. (2013), the IPCC AR4, AR5….because even those modeled, guessed-at values dispute the claims of CO2-caused OHC paradigm — which was entirely the point of the essay above. Succinctly, the claimed figures even undermine the rhetoric of the activists. Carry on. (o;
Yep, I know you know I know 🙂
“only use the stated values by Levitus et al. (2012), Gouretski et al. (2012), Rosenthal et al. (2013), the IPCC AR4, AR5….because even those modeled, guessed-at values dispute the claims of CO2-caused OHC paradigm”
That doesn’t make logical sense. If you genuinely believe those data are so wildly uncertain then they cannot be used to dispute any claims.
PaulS:
PaulS, it’s your side that believes we can determine what the 0-2000 m ocean temperatures were in the 1950s (and earlier) to the precision of hundredths of a degree. By guessing what ocean temperatures were 70 years ago (and earlier), it can be claimed that today’s OHC is dangerous and caused by CO2 concentrations.
Here is a summary of the uncertainties and error ranges in the radiation imbalance for the 2000-2010 period as they relate to estimations of ocean heat content. Carefully consider the emboldened portions below.
Stephens et al., 2012
And despite the order(s) of magnitude of uncertainty in the ocean heat flux for a well-observed period (2000-2010), you have no problem with believing we can know the values for the 1950s and earlier, and thus you can go on believing that humans are causing the modern variations in OHC?
Kenneth Richard,
You’re evading. You made the claim that these data dispute the theory. To remind: “because even those modeled, guessed-at values dispute the claims of CO2-caused OHC paradigm”.
You can believe the data are so uncertain as to be useless or you can believe they dispute the theory (regardless of whether or not your belief is correct on either count). Believing both is nonsensical.
So I’m the one evading when I’ve asked you about a half a dozen questions you’ve refused to answer? When are you going to provide the physical measurements for how much warming is caused in water by raising or lowering CO2 concentrations by 0.00001 (+/- 10 ppm)? Cite the scientific experiment verifying these results. Or do you acknowledge you don’t have any?
https://notrickszone.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/Holocene-Cooling-Pacific-Ocean-Medieval-Warm-Present-Rosenthal-13-Warmings.jpg
https://notrickszone.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/Holocene-Cooling-Pacific-Ocean-Rosenthal-13-CO2.jpg
PaulS, look at these two graphs from a peer-reviewed paper in the journal Science. It shows ocean heat content declining while CO2 concentrations are rising — a long-term inverse correlation. So do you believe that this scientific paper showing OHC for the last 10,000 years is accurate? If so, then explain why this helps substantiate your beliefs about rising CO2 causing rising OHC — since climate scientists haven’t substantiated this belief of yours.
And if you do not agree these graphs are accurate, at what point did you decide to deny science, or become a “science denier”? Because that’s what you are if you deny peer-reviewed science. Or so that’s what we are told when we question, say, the accuracy of the MBH98 hockey stick graph (that was published in the same journal).
This is exactly the choice I was talking about above. Even if I were to accept that the Rosenthal et al. (2013) paper is accurate and that we can know with good confidence what the temperatures of the 0-700 m layer were 10,000 years ago to the precision of 10ths of a degree, this still undermines the paradigm you believe in, as it shows OHC does not correlate with CO2 variations. If I don’t accept that the Rosenthal temperature values as reliable, then the paradigm you believe in is still undermined because you have no long-term evidence to support your beliefs that the OHC change in the last few decades is outside the range of natural variability. In other words, either way, your beliefs are undermined. Understand now?
Using an inability to parse sentences for sophistry won’t help your case I fear.
Here is a graphic showing the coverage of different depths in the NH and SH over time.
https://s19.postimg.org/46xcg7377/figure_42.png
As you can see, in the SH the coverage below 700m before 2003, was essentially less than 5%, and the NH was not much better.
Anyone who thinks that the ocean heat content value before 2003 was anything but a FABRICATED GUESS, really needs to go back to re-do their basic education.
“Indeed, “outcomes from modeling” are not rooted in observations — and that is entirely the problem here”
Unless you regard the scientific method as a problem then that certainly isn’t a problem. A model output is not meant to be “rooted in observations” – that would defeat the entire purpose of science. It’s supposed to make predictions which can then be checked against observations.
The basic theory predicts that rising atmospheric CO2 (and other gases) will increase Earth’s energy budget, resulting in rising surface and ocean temperatures. There is strong prima facie reason to believe this basic theory would be right since the fundamental physics of light absorption are well-established and well-quantified. It’s always possible there is a missing piece to the puzzle which negates a basic theory, which is why predictions are made and model outputs checked against observations.
However, our observations show rising surface and ocean temperatures in good agreement with model outputs. I’ve got no idea why some on here seem to think the ARGO era shows no warming: https://climexp.knmi.nl/data/inodc_temp2000_0-360E_-90-90N_n_mean1_anom_30_a.png
“However, our observations show rising surface and ocean temperatures in good agreement with model outputs.” – PaulS
Eh, …no.
http://www.c3headlines.com/2015/10/remember-when-climate-models-predicted-us-east-coast-warming-oceans.html
See more here.
http://www.c3headlines.com/are-oceans-warming/
Cherry-picking a small region of the globe and finding no warming over a cherry-picked timeframe is meaningless. Try the global average.
PaulS:
So what time period are you cherry-picking for the “global average”, PaulS? What’s your starting year? Do you think it’s acceptable to consider only a few decades worth of temperatures when there is evidence that about 95-99% of the last 10,000 years had warmer 0-700 m water temperatures than now? Or again, do you just prefer to ignore the evidence that contradicts your beliefs?
And when you talk about the “global average,” are you including the heat content below 2000 m? Because a majority of the ocean water lies below that depth, and it’s been cooling overall since the 1990s. Well, at least the tiny percentage of the coverage below 2000 m says it’s been cooling. We have no idea what most of the ocean is doing below 2000 m. Or does that not matter to you and your beliefs?
“cherry picking”????
PaulS (sod’s alter ego?) must not have looked at the rest of the material at that second link, which has links to studies from all over the world.
Also, the material at that first link wasn’t “cherry picked,” but was addressing the SPECIFIC issue of the warmunista claim that a hurricane was caused by ocean warming. The actual data show that the oceans in the path of hurricane Joquain had NOT warmed in the 75 years of temperature measurements, and also that they were most definitely NOT “…in good agreement with model outputs.”
And, again, the rest of the links present research results from all over the world, none of which are “…in good agreement with model outputs.”
Joaquin, not “Joquain”
Kenneth Richard,
“So what time period are you cherry-picking for the “global average””
No cherry-picking. You’re comparing models with observations. Model runs start around 1850-1860. Observations start around 1850-1880. Compare the full period.
“Do you think it’s acceptable to consider only a few decades worth of temperatures when there is evidence that about 95-99% of the last 10,000 years had warmer 0-700 m water temperatures than now?”
Unless you can show otherwise it’s not at all relevant to the theory if 0-700m temperatures were warmer over the past 10,000 years.
“And when you talk about the “global average,” are you including the heat content below 2000 m?”
Well, in this case the discussion concerned sea surface temperatures, so no.
“Because a majority of the ocean water lies below that depth, and it’s been cooling overall since the 1990s. Well, at least the tiny percentage of the coverage below 2000 m says it’s been cooling.”
Actually, the majority of studies addressing ocean temperatures below 2000m have found best estimate warming since the 1990s, although with substantial uncertainty.
So what time period are you cherry-picking for the “global average”
So why is it not cherry-picking to cherry-pick the 1850-1880 period when we have other estimates that date back thousands of years? Like this:
https://notrickszone.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/Holocene-Cooling-Pacific-Ocean-Rosenthal-13-CO2.jpg
Why not cherry-pick 1000 C.E.? Or for that matter, why not cherry-pick 2004 to present since that’s the period with significantly better coverage? Why does cherry-picking cease to be cherry-picking when people like you are doing the cherry-picking, but when someone else cherry-picks a starting date, that is cherry-picking. The IPCC cherry-picks the year 1951 as the first year of the critical mass of anthropogenic influence on climate. Do you consider cherry-picking 1951 as a starting point cherry-picking, or is that not cherry-picking? The IPCC also cherry-picks 1750 as the starting point for anthropogenic radiative influence. Is that year cherry-picked?
I see. So it’s not “relevant” when the CO2–>OHC connection doesn’t work for most of the last 10,000 years. It’s only “relevant” when it works for a few decades. Disregard the massive non-correlations, embrace the minuscule correlation…and claim that the minuscule correlation = 100% causation because of, uh, the scientific method. Wow, PaulS, this sounds just like real science.
This discussion/original essay has involved SSTs, 0-20 m layer (Gouretski et al., 2012), the 0-700 m layer (Rosenthal et al., 2012, Levitus et al., 2012), the 0-2000 m layer (Levitus et al., 2012), and the 2000-4000 m layer (Wunsch and Heimbach, 2014). But I understand why you’d wish to avoid discussing any more than SSTs.
Wunsch and Heimbach, 2014
“A very weak long-term [1992-2011] cooling is seen over the bulk of the rest of the ocean below that depth [2000 m], including the entirety of the Pacific and Indian Oceans, along with the eastern Atlantic basin.”
https://notrickszone.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/Holocene-Cooling-Pacific-Atlantic-Indian-Oceans-WunschHeimbach14-copy.jpg
yonason,
“The actual data show that the oceans in the path of hurricane Joquain had NOT warmed in the 75 years of temperature measurements”
This is exactly the point. There aren’t 75 years of measurements at that location. There are 160+ years. Ask yourself why 1940 was picked as the start date.
“And, again, the rest of the links present research results from all over the world, none of which are “…in good agreement with model outputs.””
And yet, if you compare the global average over the full period of record there is good agreement. How do you think that happens?
PaulS:
The scientific method requires observational, physical evidence. You have no observational, physical evidence that CO2 concentration variations heat or cool water. Therefore, the scientific method does not apply here.
I am glad that you have decided to properly call it a belief (“believe”). Beliefs aren’t science, PaulS. Even calling it a “basic theory” would imply that you have observational evidence that CO2 concentration variations heat or cool water. And you have none. Therefore, you can’t even call it a “theory.” Nor can you call it an hypothesis, as hypotheses require observational evidence as well.
PaulS, if we don’t have observational, physical evidence, it is not science. You have no observational, physical evidence that CO2 concentration variations heat or cool water. None. We don’t even have long-term correlation evidence. Therefore, any statement about what you think might be true because that’s what the models say is no more than an assumption. I asked you to provide observational, physical evidence (i.e., scientific evidence) that CO2 atmospheric changes in volumes of +/- 0.000001 heat or cool water. Obviously, you didn’t — and can’t. Why? Because none exists. Your entire paradigm is rooted in belief, not science.
Does the 1,000- to 10,000-year history of centennial -scale plummeting ocean heat content (Rosenthal et al., 2013) while CO2 concentrations are rising (i.e., an inverse correlation) appear to be in “good agreement with model outputs”, or do you think it’s best just to ignore the paleoclimate evidence that doesn’t fit your beliefs about CO2 concentrations heating up the oceans when they rise?
Kenneth Richard,
“Therefore, the scientific method does not apply here”
You fundamentally misunderstand science and the scientific method. The whole point is to make predictions and check against observations. Climate models predicted that ocean and surface temperatures would rise with increasing CO2 concentration. We observe that ocean and surface temperatures have risen as CO2 has increased. That’s science.
“I am glad that you have decided to properly call it a belief (“believe”). Beliefs aren’t science”
Again, your fundamental lack of science-literacy is betrayed. There is no absolute proof in science. Therefore all scientific knowledge is belief. We believe that general relativity is a good representation of the universe. We can never prove it absolutely. Science is about building beliefs backed by evidence, but it is always belief nonetheless.
Wow. So in your view, the scientific method means that we make a prediction about what we think might happen given two variables, and if what we think will happen actually happens (we think, maybe), then the scientific method has been applied, because we can then confirm scientifically that one variable was the cause of the other variable. Correlation = causation. On what universe is this the scientific method?
So we have one variable, atmospheric CO2 concentration. It has changed by 0.0001 (100 parts per million) since 1900. We have another variable, ocean heat content (0-4000 m). Despite massive error and uncertainty in measurement, we assume that it has warmed by 0.09 C in the 0-2000 m layer since 1955 (Levitus et al., 2012). We effectively have no idea what the values are for the pre-1955 data, and we don’t know what the values were below 2000 m either. Regardless, because the CO2 concentration has increased, and we think the 0-2000 m layer OHC has increased, therefore it has been scientifically confirmed that the 0.0001 change in atmospheric CO2 concentration was the cause of the 0.09 C increase in OHC since 1955. Again, correlation = causation. And this, to you, is the scientific method. Science.
During the 1700s, there were, on average, 1,000 pirate ships sailing the Atlantic on any given day during the months of April through September. During the 1800s, there were 300 pirate ships on the Atlantic. During the 1900s, it was down to 50. During the 1700s and 1800s, the Atlantic was -0.3 C colder than it was during the 1900s. The models say that higher pirate ship concentrations cause cooling, and lower pirate ship concentrations cause warming. We have no observational evidence or physical measurements or controlled scientific experiments attesting to the pirate ship-water temperature correlation, but that’s okay…it’s a model. Therefore, using the scientific method as you’ve applied it, it can be confirmed that higher pirate ship concentrations on the Atlantic cause cooling, and lower pirate ship concentrations on the Atlantic cause warming. We have a correlation between two variables; therefore, we have cause. The science says that pirate ship concentrations cause the ocean to warm or cool. Again, the scientific method. Science.
https://notrickszone.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/Holocene-Cooling-Pacific-Ocean-Medieval-Warm-Present-Rosenthal-13-Warmings.jpg
What was the reason the ocean heat content plummeted after the Medieval Warm Period, PaulS (graph above)? I’ve asked you this many times, and you refuse to answer. CO2 concentrations rose, and yet OHC declined during this period. In fact, in looking at this graph, while there was an overall long-term decline, we see there were about 11 warming periods between 1100 and 1800 that either matched or exceeded the amplitude of the 20th/21st century warming. None of those previous warming periods were connected to CO2 concentration changes. So why is it your belief that the “scientific method” of the CO2-OHC connection applies to the most recent warming event, but not to those other ones?
AndyGG,
Is it still 2008 where you are?
Paul S.. have you finished high school yet ?
Or are you still on your third attempt.
“Unless you regard the scientific method as a problem….”
The scientific method would require the validation of the models against reality.
Big Barn… OOPs… missed !!!
There are very strong reasons to KNOW that the basic AGW hypothesis is WRONG !!!
“I’ve got no idea why some on here seem to think the ARGO era shows no warming”
roflmao….
See that flat bit after 2004. !!
That is the measured bit
http://static.skepticalscience.com/images/robust_ohc_lyman1.gif
AndyGG,
Is it still 2008 where you are?
*posted in wrong thread before
Translate it to degrees, bozo.
You are fooling only yourself.
Here’s one that goes to 2012..
Notice anything ?
http://3.bp.blogspot.com/-zlcxrtdLa8Q/T46Kj82y_PI/AAAAAAAAB5k/6f8T9nwoep8/s1600/image%2BArgo%2Bheat%2Bdata%2Bplot%2B%2B2012.png
Paul S, do you reckon they can really measure total ocean heat to 0.1C?
SST’s …. OOPS !!
http://www.tropicaltidbits.com/analysis/ocean/global.png
PaulS writes
“There is strong prima facie reason to believe…”
two comments on the term “prima facie.”
1. I have two degrees in scientific disciplines, one undergrad and one grad. I have NEVER heard that term used in any of my classes or any of my work. It isn’t a scientific term.
2. “Prima facie evidence is a legal term used to mean that you have enough evidence to prove something by pointing to some basic facts, but that your proof can be refuted.”
Read more at http://www.yourdictionary.com/prima-facie-evidence#s54kjCrQutOW0fy6.99
LOL – If it “can be refuted” then it isn’t a rigorous proof, nor is it the “settled science” they all want us to believe it is.
Interesting how they don’t even know the meaning of the words they use, but they want us to believe they understand the science.
@PaulS 10. November 2016 at 12:43 AM
“Ask yourself why 1940 was picked as the start date.” – PaulS
(I addressed this then, but my post never appeared, so here’s a redo)
CO2 didn’t appear to start increasing until 1940.
https://notrickszone.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/CO2-Emissions-1900-2014-GtC-per-year-Climate-Laws.jpg
What the temps did before CO2 began to rise isn’t relevant to this analysis. It’s not “cherry picking” to only include relevant data.
CO2 rose for 75 years but temps remained constant despite modeling that showed they should go up dramatically.
http://c3headlines.typepad.com/.a/6a010536b58035970c01b8d16250d4970c-pi
Warming hypothesis, i.e., that warming is due to CO2, has been falsified.
Again, I remind you that they told us that hurricane Joaquin was caused by a man made increase in CO2 (unproven assertion) which caused ocean temps to rise. Since the temps didn’t rise, though, it is impossible that could have been the cause, so that was a false claim which some might even call “a lie.”
“…if you compare the global average over the full period of record there is good agreement.”
Again, no. But feel free to try to prove it, with real data (include credible references to your material). Good luck.
Remember, you are responsible for proving what you assert. I am under no obligation to disprove your false assertions, especially since you are too lazy to bother trying to prove them.
Where’s my post. It was a redo of one that never appeared about a week ago. I don’t want the original now, just this one, since I edited it substantially, but it would be nice to see something. (this is just one of 3 that haven’t appeared, but those were only relevant to when I posted them, so it wouldn’t matter now.
Thanks