AMO cycle on the downward side: Red Sea to cool in the coming decades
By Die kalte Sonne
(German text translated by P Gosselin)
Seven years ago, in our book “The Forgotten Sun”, we proposed using ocean cycles for medium-term forecasts. At the time, the climate establishment was strictly opposed to this. Today fortunately times have changed.
On March 15, 2019, a team led by George Krokos analyzed the temperature development of the Red Sea in Geophysical Research Letters, which has become noticeably warmer in recent decades. The researchers put this into a long-term context and found a strong correlation with the 70-year ocean cycle of the AMO (Atlantic Multidecade Oscillation).
Now that AMO has reached its peak, Krokos and colleagues expect the Red Sea to cool in the next three decades. Abstract:
Natural Climate Oscillations may Counteract Red Sea Warming Over the Coming Decades
Recent reports of warming trends in the Red Sea raise concerns about the response of the basin’s fragile ecosystem under an increasingly warming climate. Using a variety of available Sea Surface Temperature (SST) data sets, we investigate the evolution of Red Sea SST in relation to natural climate variability. Analysis of long‐term SST data sets reveals a sequence of alternating positive and negative trends, with similar amplitudes and a periodicity of nearly 70 years associated with the Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation. High warming rates reported recently appear to be a combined effect of global warming and a positive phase of natural SST oscillations. Over the next decades, the SST trend in the Red Sea purely related to global warming is expected to be counteracted by the cooling Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation phase. Regardless of the current positive trends, projections incorporating long‐term natural oscillations suggest a possible decreasing effect on SST in the near future.”
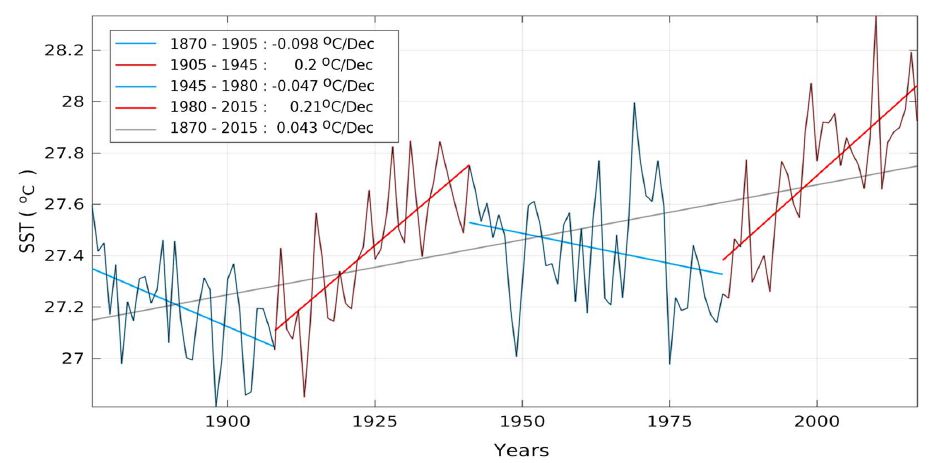
Figure: Temperature of the Red Sea. Data: Hadley Centre. Figure: Krokos et al. 2019





For nigh-on half a century, so-called “climate models” have notoriously been no more than rudimentary linear extrapolations, studiously ignoring not only astro-geophysical effects (axial precession, cosmic rays, geothermal flux, plate-tectonic dispositions, total solar irradiance [TSI]) but episodic catastrophes such as cometary/meteorite strikes (Chixculub, Younger Dryas) and orogenic volcanism (Ural mountain-building in the Permian, Andean-Rocky Mountain [Laramide] upheavals in Tertiary/Paleogene [Eocene, Oligocene] times).
In October 2018, Russian researcher Valentina Zharkova presented her Climate – Solar Magnetic Field (C-SMF) correlation model to Britain’s Global Warming Policy Foundation (GWPF). So much for “consensus”: Nine months later, out of 150 models Zharkova’s was one of only two correctly predicting that Solar Cycle 24 (serialized from 1755) would prove much weaker than Cycle 23 (ended December 2008, 12.3 years from August 1995).
Not only does Mde. Zharkova’s work make nonsense of hyper-politicized Green Gang “anthropogenic warming”, but from December 2017 Australian researcher Robert Holmes’ peer-reviewed Molar Mass Version of the Ideal Gas Law has definitively refuted any possible CO2 connection to climate variations: Where GAST Temperature T = PM/Rp, any planet’s near-surface global Temperature derives from its Atmospheric Pressure P times Mean Molar Mass M over its Gas Constant R times Atmospheric Density p.
Applying Holmes’ relation to all planets in Earth’s solar system, zero error-margins attest that there is no empirical or mathematical basis for any “forced” carbon-accumulation factor (CO2) affecting Planet Earth.
[…] Read more at No Tricks Zone […]
[…] https://notrickszone.com/2019/07/07/red-sea-temperature-record-shows-it-follows-the-amo-not-co2-natu… […]
[…] Red Sea Temperature Record Shows It Follows The AMO, Not CO2 … “Natural Climate Oscillations… […]
[…] https://notrickszone.com/2019/07/07/red-sea-temperature-record-shows-it-follows-the-amo-not-co2-natu… […]
[…] https://notrickszone.com/2019/07/07/red-sea-temperature-record-shows-it-follows-the-amo-not-co2-natu… […]
[…] P. Gosselin, July 7, 2019 in […]