Oceans Warmed 6 Times Faster Than
Modern Rates During The Mid-Holocene
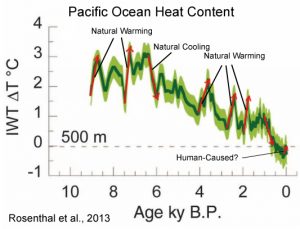
Annotated graph from Rosenthal et al. (2013) illustrating the steep amplitude of natural variations in ocean heat
It has long been acknowledged by scientists that significant changes in deep ocean heat content have occurred in the past in the absence of changes or forcing from CO2. Stott et al. (2007), for example, conclude that deep ocean temperatures rose by 2°C within a 2,000-year time span (19,000 to 17,000 years ago) about a 1,000 years before CO2 concentrations (and surface temperatures) began to rise.
Deep sea temperatures warmed by ~2C between 19 and 17 ka B.P., leading the rise in atmospheric CO2 and tropical surface ocean warming by ~1000 years.
Similarly, Demezhko and Gornostaeva (2015) found that the heat energy change in the deep oceans during the climate transition from the last ice age to this current interglacial occurred “2-3 thousands of years” before the increases in surface temperature and CO2, and that “the increase of carbon dioxide may be a consequence [rather than a cause] of temperature increasing”. The authors then acknowledge that this suggests that there was “no significant contribution of CO2 forcing to climatically caused heat flux and thus to the temperature increase during the Pleistocene-Holocene warming”.
Demezhko and Gornostaeva, 2015
Despite the substantial dispersion of CO2 estimations, a character and a chronology of CO2 concentration changes are much closer to temperature changes rather than to heat flux variations. It may mean no significant contribution of CO2 forcing to climatically caused heat flux and thus to the temperature increase during Pleistocene–Holocene warming. About 10 kyr BP the increase of carbon dioxide concentration was replaced by its fall which ended about 8 kyr BP. This local minimum [in CO2 concentration] is not consistent with either GST [ground surface temperature] or SHF [surface heat flux] histories. … The reconstructed surface heat flux reflects impact of all possible sources of radiative forcing. In addition to solar insolation, greenhouse gases (such as CO2) can be a source of additional forcing. On the other hand the increase of carbon dioxide may be a consequence of temperature increasing. Comparing the chronology of surface flux, temperature and carbon dioxide concentration changes, we can draw some conclusions about the causes of climate change. … The increase of carbon dioxide concentrations occurred 2–3 thousands of years later than the heat flux increase and synchronously with temperature response.
Scientists Ellis and Palmer (2016) get right to the point and conclude CO2 plays “little or no” role in forcing the warming during interglacial periods…
Conclusion: [I]nterglacial warming is eccentricity and polar ice regrowth regulated, Great Summer forced, and dust-ice albedo amplified. And the greenhouse-gas attributes of CO2 play little or no part in this complex feedback system.
….while scientists Douglass and Knox (2014) identify the source of modern deep ocean temperature forcing that has an “unquestionably solar origin” manifested by El Niño/La Niña phenomena.
Global ocean temperature time series from the surface to depths of 2000 m since the year 2000 are found to agree in detail with those of other diverse climate indices. It is asserted that these systems are driven by a forcing unquestionably of solar origin that has two manifestations: (1) a direct phase-locked response to what is identified as a solar forcing at a frequency of 1.0 cycle/yr for the whole time series; (2) a second phase-locked response at a period of two years or three years. With these findings it is becoming clear that the entire climate system is responding to the varying incident solar radiation… The most prominent manifestations of the pattern are found in the El Niño/La Niña phenomena.
Advocates of the assumption that CO2 variations are a primary cause of changes in deep ocean heat content (i.e., those who author government-sponsored IPCC reports and activists for the anthropogenic global warming cause) have necessarily believed that past natural variations in deep ocean heat content are very slow and gradual. They have presumed that the forcing from Milankovitch cycles (changes in solar radiation absorbed by the Earth’s surface due to orbital variations) are the cause of deep ocean changes over time, but that these changes occur only as slowly as orbital variations occur — on millennial scales (“several thousand years“), not in decades to centuries. In this way, they can deny that the Sun plays a role in modern climate changes…despite burgeoning evidence to the contrary. The Stott et al. (2007) finding that deep oceans warmed at a rate of 1°C/1,000 years referenced above would be consistent with these assumptions.
New Paper: ‘Rapid variations in deep ocean temperature detected in the Holocene’
Brown University geologist Samantha Bova and her colleagues reach a different conclusion, however, in a paper just published online for the prestigious journal Geophysical Research Letters. These scientists have found that, in the absence of any significant CO2 concentration changes or human influence during the Holocene (i.e., the last ~10,000 years), the deep oceans naturally warmed by more than 2°C in a span of just 200 years, which is several times the rate in which they are alleged to have warmed in the last ~60 years of the supposedly dominant anthropogenic influence on climate. In fact, Bova et al. (2016) conclude that deep ocean temperature changes for the last 200 years are apparently so negligible they are “below the detection limits”.
The observational record of deep-ocean variability is short, which makes it difficult to attribute the recent rise in deep ocean temperatures to anthropogenic forcing. Here, we test a new proxy – the oxygen isotopic signature of individual benthic foraminifera – to detect rapid (i.e. monthly to decadal) variations in deep ocean temperature and salinity in the sedimentary record. We apply this technique at 1000 m water depth in the Eastern Equatorial Pacific during seven 200-year Holocene intervals. Variability in foraminifer δ18O over the past 200 years is below the detection limit [a change in ocean heat cannot be detected in the past 200 years], but δ18O signatures from two mid-Holocene intervals indicate temperature swings >2 °C within 200 years.
According to the IPCC (2013), 93% of the heat energy in the climate system claimed to be due to anthropogenic global warming is found in the oceans (AR5, Chapter 3). Levitus et al. (2012) estimate that the heat energy change (converted to temperature) amounted to an increase of just +0.09°C between 1955 and 2010 in the upper 2000 meters of the ocean, or less than one-tenth of one degree over 55 years.
The World Ocean accounts for approximately 93% of the warming of the earth system that has occurred since 1955. … The heat content of the World Ocean for the 0–2000 m layer increased by 24.0 ± 1.9 × 1022 J (±2S.E.) [over 1955-2010] corresponding to a rate of 0.39 W m−2 (per unit area of the World Ocean) and a volume mean warming of 0.09°C.
Again, natural variation in ocean temperatures may reach amplitudes of + or – 1°C every 100 years without any external forcing from anthropogenic CO2 emissions. So if 93% of the change forced by the alleged human climate influence has only produced a temperature change of hundredths to tenths of a °C in the deep oceans since 1955, or since CO2 concentrations rose by about 75 parts per million (315 ppm in 1955 to 390 ppm in 2010), this would clearly indicate that it is extremely difficult if not effectively impossible to confidently attribute the practically imperceptible change in ocean temperature to anthropogenic CO2 emissions, or to CO2 in general.
More succinctly, if deep ocean temperatures can naturally rise by 1°C in 100 years without any change in CO2, then attributing changes in ocean temperature that are already “below the detection limit” for the last 200 years (or just ~0.1°C since 1955) to anthropogenic CO2 forcing is highly presumptuous at best.
And if 93% of the heat from “global warming” cannot be attributed to humans with any degree of confidence, then there is necessarily no such conceptualization of anthropogenic global warming that could be claimed to have been affirmed scientifically. Effectively, if we cannot detect an anthropogenic signal in deep ocean heat data, anthropogenic global warming would necessarily be characterized as a belief, not a scientifically confirmed hypothesis.





Currently Gavin tells me we are having the hottest year ever, what he fails to acknowledge is we are in one of the colder periods in earth’s history.
Only in the last 10,000 years ie. the current interglacial. 🙂
just in case of confusion, I was replying to this statement from tom0mason
“we are in one of the colder periods in earth’s history”
We are, of course, only a small molehill above the COLDEST period in the whole of those 10,000 years.
And that slight warming has been HIGHLY BENEFICIAL, lifting the world out of truly desperate times..
I assumed that is what you meant AndyG55
Gavin is lying. The Holocene had spells that were much warmer.
He is factually challenged, that’s for sure.
http://hockeyschtick.blogspot.com/2010/04/nasas-gavin-schmidts-lies-damned-lies.html
P Gosselin wrote:
“The Holocene had spells that were much warmer.”
When?
Does it never even occur to you people that you have to PROVE what you claim??
Here are over 50 graphs from all over the globe that show modern temperatures are not only not unusual, they are cooler than some periods that occurred during the Little Ice Age. Since this post was made, an additional 27 graphs (80 graphs accumulated as of now) do not support the belief that modern temperatures are unusual or unprecedented. What caused all those past warming periods, David?
https://notrickszone.com/2016/09/27/hide-the-decline-unveiled-50-non-hockey-stick-graphs-quash-modern-global-warming-claims/
Richard: Which graphs?
Denying history and science yet again, hey rotten-appell.
When Pierre?
You don’t seem to have an answer.
Don’t forget, Gavin manipulates the numbers too…just ask Tony Heller
By your (wrong) definition, UAH “manipulates” the numbers too — their satellite data model is far more complicated than GISS;s model, in fact.
Gavin says ‘in the record,’ dummy.
This is the process whereby solar changes alter global cloudiness so as to change the amount of energy entering the oceans and thereby skew the balance of ENSO between El Nino warming or La Nina cooling:
http://joannenova.com.au/2015/01/is-the-sun-driving-ozone-and-changing-the-climate/
as impliedly envisaged in the above paper.
Defunding GISS should eliminate one bunch of liars.
“Defunding GISS should eliminate one bunch of liars.”
yes, destroying the data is a very good idea, if you just want to be a merchant of doubt.
GISS temperature is NOT data it is FABRICATION.
It is a LIE, and should be removed from any pretence of being science.
GISS takes data and homogenizes it. They are destroying information. Their product is worth less than any of the thermometers that went into it.
Why does NASA GISS not use ONE satellite? Why is NASA doing this?
Well you and I know the answer. Because warmunism brings in 1.2 billion USD tax money a year for NASA. So they have Gavin promote the scare.
Nothing that he does has ANYTHING to do with data. Or science.
DirkH wrote:
“Why does NASA GISS not use ONE satellite? Why is NASA doing this?”
How can satellites measure surface temperatures?
Huh Dirk?
DirkH says:
“GISS takes data and homogenizes it. They are destroying information.”
How so? Specifically?
Sod,still making dumb comments,since it is well known that GISS temperature sets,are a pile of crap.
Really? What are your qualifications for saying so?
GC, GISS knows far, far, far ….^100 times more than you do.
You can’t even find the missing 150 W/m2 from the Earth’s energy balance. Ha.
The basic understanding that our ‘climate scientists™’ should have is water on this planet is he control knob for how much of the sun’s heat is absorbed and released and over what time period.
CO2 just gets the plants to grow.
tom0mason wrote:
“The basic understanding that our ‘climate scientists™’ should have is water on this planet is he control knob for how much of the sun’s heat is absorbed and released and over what time period.”
Prove this.
I don’t think you can.
The IPCC says that 93% of the heat in the climate system is found in the oceans. Just 1% of the heat in the climate system is in the air. As you know, though, CO2 doesn’t heat water. (If you think it does, please cite the scientific experiment that demonstrates this.) So if 1% of the heat from global warming is manifested in air temperatures, and 93% in manifested in ocean temperature changes according to the IPCC, why do you think it is up to “tom0mason” to “prove” that the oceans are the control knob, since he is just reaffirming what even the IPCC already effectively says? Why do you think the 93% does not “control” the 1%, especially since the heat capacity of the ocean is more than 1,000 times greater than the air? Prove that the air heats the oceans, David.
Kenneth Richard says:
“The IPCC says that 93% of the heat in the climate system is found in the oceans.”
Wrong. It says about 93% of the trapped heat goes into the ocean.
No, David, the IPCC doesn’t use your wording, especially the words “trapped heat” together.
Here are the exact words from AR5: “Ocean warming dominates the total energy change inventory, accounting for roughly 93% on average from 1971 to 2010.”
And here’s where they got that from (Levitus et al., 2012): “The World Ocean accounts for approximately 93% of the warming of the earth system that has occurred since 1955.”
Interestingly, the latter quote sounds eerily similar to what I wrote: “93% of the heat in the climate system is found in the oceans.”
Neither quote appears to be all that similar to what you wrote, though: “about 93% of the trapped heat goes into the ocean.”
Kenneth says:
“As you know, though, CO2 doesn’t heat water. (If you think it does, please cite the scientific experiment that demonstrates this.)”
“Observational determination of surface radiative forcing by CO2 from 2000 to 2010,” D. R. Feldman et al, Nature 519, 339–343 (19 March 2015)
http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v519/n7543/full/nature14240.html
Press release for Feldman et al: “First Direct Observation of Carbon Dioxide’s Increasing Greenhouse Effect at the Earth’s Surface,” Berkeley Lab, 2/25/15
http://newscenter.lbl.gov/2015/02/25/co2-greenhouse-effect-increase/
David, I’ve read and cited Feldman et al. (2015) myself many times (for reasons that completely undermine your beliefs), and it is patently obvious that that paper doesn’t even mention the words “ocean” and “heat” together. It isn’t even close to being a paper offering observational evidence that CO2 heats water. It’s a paper entirely built upon models of radiative forcing that are rooted in assumptions, not observational evidence. As I suspected, you cannot cite any scientific evidence that varying CO2 up or down over a body of water in volumes of 0.000001 (1 ppm) cause heat changes in bodies of water. None. All you have are models. Models aren’t observational evidence.
And anyway, according to the Feldman paper, the +0.000022 (22 ppm) increase in atmospheric CO2 concentration during 2000-2010 elicited a RF value of 0.2 W m-2 during those 10 years. According to Stephens et al. (2012), the radiative imbalance for the same 2000-2010 period was estimated to be +0.6 W m-2 (with an uncertainty of 17 W m-2, which is more than 10 times greater than the assumed forcing for both the radiative imbalance and the estimate of forcing attributed to CO2). A radiative imbalance of 0.6 W m-2 over 2000-2010 means that CO2 only caused 33% (0.2 of 0.6 W m-2) of the radiative forcing for that period. That means that something other than CO2 was the predominant radiative forcing (0.4 W-2). What was it, David?
Worse (for you), Song, Wang, and Tang (2016), a more recent paper entitled “A Hiatus of the Greenhouse Effect”, finds that there was no (a “trendless”) radiative forcing (essentially 0 W m-2) from the CO2 greenhouse effect from 1992 to 2014:
The oceanic Gaa [atmospheric greenhouse effect] exhibits a notable increasing trend with a rate of 0.21 W m−2 yr−1 in 1979–1991, whereas its rate of change (−0.04 W m−2 yr−1) during 1992–2014 is not statistically significant. By contrast, although a sudden change in the Gaa tendency is observed overland, the breakpoint is approximately 5 years later than that of the oceanic Gaa. The terrestrial Gaa trends are 0.12 W m−2 yr−1 and 0.05 W m−2 yr−1 before and after 1997, respectively.
In the last subperiod [2003-2014], the global averaged SULR [surface upwelling longwave radiation/greenhouse effect] anomaly remains trendless (0.02 W m−2 yr−1) because Ts [global temperatures] stop rising. Meanwhile, the long-term change of the global averaged OLR anomaly (−0.01 W m−2 yr−1) is also not statistically significant. Thus, these two phenomena result in a trendless Gaa [atmospheric greenhouse effect].
I’ve asked you to provide observational, experimental, scientific evidence (complete with actual physical measurements) that + or – 0.000001 variations in CO2 cause net changes in ocean heat many times now. You have, once again, failed to do so. Instead, the best you can do is cite a paper that doesn’t even mention the ocean. I guess that is to be expected, considering your track record.
Kenneth wrote:
“…why do you think it is up to “tom0mason” to “prove” that the oceans are the control knob”
Simple — he made that claim. Hence he must prove it, with evidence, or it will be dismissed.
Volumetric heat capacity of water = 4.1796 J•cm−3•K−1
Volumetric heat capacity of air = 0.00121 J•cm−3•K−1
It takes 3,454 times more energy to heat up 1 liter of water than it does to heat up 1 liter of air.
Volume of the world’s oceans = 1.338 billion km3
Volume of the world’s atmosphere = 4.177 billion km3
It would take 1,106 times more energy to raise the temperature of the earth’s oceans by 1°C than it would to raise the temperature of the earth’s atmosphere by 1°C.
And yet it is your claim that the heat in the air is the control knob for the heat in the ocean. Prove it, David.
Murray et al., 2000
“net surface heat flux is almost always from ocean to atmosphere”
Minnett et al., 2011
“the heat flux is nearly always from the ocean to the atmosphere“
Ellsaesser, 1984
“the atmosphere cannot warm until the oceans do.”
Kenneth wrote:
“Why do you think the 93% does not “control” the 1%, especially since the heat capacity of the ocean is more than 1,000 times greater than the air?”
Why is the 93% gaining heat at such a rapid pace?
Um, David, a 0.09 C change in 55 years (Levitus et al., 2012) is not even close to being “rapid” relative to natural variability. Did you even read this essay at all? Changes of more than 2 C in 200 years occur naturally and without CO2 flux. What causes those (truly) rapid changes, David? If you’d rather not read, look at the pictures: https://notrickszone.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/Holocene-Cooling-Pacific-Heat-Content-Rosenthal13-copy.jpg
How did they measure deep water temperature 200yrs ago.
They have to use very rough proxies for temperature changes…
“Here, we test a new proxy – the oxygen isotopic signature of individual benthic foraminifera – to detect rapid (i.e. monthly to decadal) variations in deep ocean temperature and salinity in the sedimentary record”
Even in the ARGO era (2003- ), the error bars and uncertainty ranges for our educated guesses (that’s what they are) about deep ocean heat are 10 times greater (and more) than the suggested temperature changes (hundredths of a degree) themselves. In other words, we really have no idea, making the suggestion that we are in some sort of “unprecedented” time with regard to ocean heat all the more dubious.
Notice that the proper science papers say approximately X degrees.
Yet the heat content from 1955 is suddenly done to 1/100th of a degree.
Someone is pulling their own chain.
Kenneth Richard wrote:
“Even in the ARGO era (2003- ), the error bars and uncertainty ranges for our educated guesses (that’s what they are) about deep ocean heat are 10 times greater (and more)”
Argo doesn’t measure deep ocean heat content. It’s limited to 0-2000 m.
“How did they measure deep water temperature 200yrs ago.”
They didn’t.
The ocean data starts in about 1955. Read Levitus.
Actually, the ARGO data start in 2003. And the satellite altimetry data start in 1993. And the sea ice data start in 1979. So now we know that today’s climate is unprecedentedly warmer than at any time in the last 10,000 years. Because we have all the data we need to compare.
http://science.sciencemag.org/content/342/6158/617.abstract
We show that water masses linked to North Pacific and Antarctic intermediate waters [0-700 m] were warmer by 2.1 ± 0.4°C and 1.5 ± 0.4°C, respectively, during the middle Holocene Thermal Maximum than over the past century. Both water masses were ~0.9°C warmer during the Medieval Warm period than during the Little Ice Age and ~0.65° warmer than in recent decades.
““The ocean data starts in about 1955.””
ROFLMAO.. You really are a low-level clown, Appell.
There is basically no real data before 2003.
Levitus is all models, based on assumptions.
https://s19.postimg.org/46xcg7377/figure_42.png
Less than 20% cover of the whole SH before 2003.
And goodness knows what quality that would have been.
Heck, that’s even worse than the current surface data !!
Stephen Richards said:
“How did they measure deep water temperature 200yrs ago.”
Who do you cite as having done this?
Do you even read the articles that you comment on, David (where the answer to your question is found)? Or do you just immediately go to the comment section to drop glib missives?
No one says they did.
2016 looks like a hottest year in the UAH data as well.
After making up a “la nina” effect that co9uld keep this from happening, Roy spencer decided to change tune and now is arguing that the difference will not be big.
Why would facts matter?
http://www.drroyspencer.com/2016/12/uah-global-temperature-update-for-november-2016-0-45-deg-c/
“2016 looks like a hottest year in the UAH data as well”
Thank goodness the RECOVERY from the LIA, the COLDEST period in the last 10,000 years still continues, even if it is ONLY caused by two El Nino events.
Still almost certainly cooler than the REAL temperatures of around 1930-1940, and certainly cooler than the MWP and the first 3/4 or more of the current interglacial.
This year is purely down to the TRANSIENT affect of the El Nino, and I’m sure you know that. But it is all you have, El Nino warming, so I guess your foolishness will continue.
There will be no El Nino next year. Remember that.
If you want it COLD..
Move out of your inner-city greenie ghetto and move to Siberia.
I dare you
He could move to Northern Germany and lose 5 deg C. He’s in the hottest part of Germany. Or he could move uphill 100 m and lose 1 deg C.
But that would be simple and cheap. We don’t want solutions that work. We want 35 billion EUR a year redistribution. In Germany alone.
“He’s in the hottest part of Germany.”
By choice.. we chooses WARM,
…. then complains about it… DOH !!!
A clown, without a doubt.
Siberia, sop. Go somewhere where the slight, but highly beneficial warming, will never reach you.
Huh? “Making up” a La Nina effect? sod, the La Nina has only just begun. The effects could last a full year, even two. These are monthly averages, anomalies from the mean that don’t always go in one direction from one month to the next. Did you realize that the La Nina effect after the ’97-’98 Super El Nino lasted through ’99 and ’00? The 1998 anomaly (whole year) is the equivalent of 2016. Temperatures will drop in 2017 and ’18 just like they did in ’99-’00. They already have over land by -1.2 C (RSS) in the last 8 months. It’s predictable – because ENSO cycles are natural phenomena, not driven by anthropogenic CO2 emissions.
Kenneth: false — no La Nina has begun. And you have no evidence that it has.
In any case, it, like the El Nino, is a natural phenomena, while influenced by AGW.
So what was the cause (physical mechanism) of the 1.2 C temperature drop over land in the last 8 months? https://notrickszone.com/2016/11/17/satellites-show-1-2-c-temperature-drop-since-early-2016-as-scientists-project-low-solar-activity-cooling-in-coming-decades/
Explain how CO2 concentrations “influence” tradewinds and changes in near-surface and deep ocean temperatures. Cite scientific papers detailing the physical process whereby CO2 variations cause heat changes in water.
Kenneth wrote:
“So what was the cause (physical mechanism) of the 1.2 C temperature drop over land in the last 8 months?”
Cooling from the ending of an El Nino.
There is no data showing a La Nina is here.
Source:
http://www.cpc.ncep.noaa.gov/data/indices/wksst8110.for
“Cooling from the ending of an El Nino.”
So what percentage of the warming from the El Nino was caused by humans? What percentage of the cooling after the El Nino warming ended was caused by humans? Please provide scientific evidence to support your answer.
Another weather thinking comment from Sod,god when is he ever going see the climate more often?
May I ask you learned gentlemen what ‘deep’ means in reference to oceans? Can any warming be attributed to the subduction zones at the edges of continental plates ? Would these be deep enough or are there ocean “deeps” which are lower?
New Zealand is a tectonically active area where the plates move over or under each other. Is heat generated by these into the oceans and moved by convection. Can this be detected by proxy data to coincide perhaps with known earth movements? If a lot of movement happens is there a warm current generated.
In the paper specifically referenced for this essay (Bova et al., 2016), the deep ocean is defined as 1,000 meters deep. The top graph (from Rosenthal et al., 2013) is 500 meters in depth. The Levitus et al. (2012) joules/temperature values referenced above refers to depths of 2,000 meters. Generally, any depth below about 500 meters is considered the “deep ocean”.
For the record, more than half (52%) of ocean waters lie below the 2000 meter depth, so calling the 500-2,000 meter layer the “deep ocean” is still quite relative.
deep means < -2000 m generally. But different authors often use their own definitions.
M E 2 wrote:
“May I ask you learned gentlemen what ‘deep’ means in reference to oceans?”
“Deep” usually means > 2000 m. Some scientists, like this summer’s paper by Greg Johnson, used > 1800 m.
M E 2 wrote:
“Can any warming be attributed to the subduction zones at the edges of continental plates ?”
Good question, but, no, it’s way too small of an area. The ocean is vast!, 1,335 Mkm3.
OT – Hurricane (Cyclone) season in the Northern Hemisphere is over for the year.
http://www.nhc.noaa.gov/
According to my records, YTD ACE (through Nov) is 9th highest in 47 years.
PS: ACE is a horribly metric, but one people keep insisting on.
“According to my records”
I doubt there is anyone here who is relying on you for information or records.
Why do you end comments on older threads?
This entire post deliberately tries to hide the fact that it’s not temperature that matters, it’s change in ocean heat content. That’s what will drive future warming.
And the OHC is increasingly enormously.
0-700 m region of global ocean since 1Q1955: +177 ZJ (delta-T = +0.17)
0-2000 m region of global ocean since 1Q2005: +120 ZJ (delta-T = +0.04 C).
Didn’t you take introuctory thermodynamics, Pierre?
* ZJ = Zettajoule = 10^21 J.
Gavin and Co. at Real Climate say the opposite of what you did. Does that mean that they’re wrong, or you?
http://www.realclimate.org/index.php/archives/2014/10/ocean-heat-storage-a-particularly-lousy-policy-target/comment-page-2/
Ocean heat content has no direct relation to any impacts.
Ocean heat content has increased by about 2.5 X 1023 Joules since 1970 (IPCC AR5). What would be the impact of that? The answer is: it depends. If this heat were evenly distributed over the entire global ocean, water temperatures would have warmed on average by less than 0.05 °C (global ocean mass 1.4 × 1021 kg, heat capacity 4 J/gK). This tiny warming would have essentially zero impact. The only reason why ocean heat uptake does have an impact is the fact that it is highly concentrated at the surface, where the warming is therefore noticeable (see Fig. 1). Thus in terms of impacts the problem is surface warming – which is described much better by actually measuring surface temperatures rather than total ocean heat content. Surface warming has no simple relation to total heat uptake because that link is affected by ocean circulation and mixing changes. (By the way, neither has sea-level rise due to thermal expansion, because the thermal expansion coefficient is several times larger for warm surface waters than for the cold deep waters – again it is warming in the surface layers that counts, while the total ocean heat content tells us little about the amount of sea-level rise.)