Scientists report they must “exclude atmospheric pCO2 as a direct driver of SST variations” after finding the Atlantic Ocean’s surface was multiple degrees warmer than today from 90 to 20 thousand years ago, or when CO2 concentrations hovered below 200 ppm.
Another new study (Hou et al., 2020) casts even more doubt on the contention that CO2 concentrations are a driver of ocean temperature changes. Sea surface temperatures ranged between 1 and 5°C warmer than today throughout the last glacial period in the western tropical Atlantic.
“Our results indicate a lack of pronounced glacial-interglacial variability in the SST record, prompting us to exclude atmospheric pCO2 as a direct driver of SST variations in the southern WTA [western tropical Atlantic].”
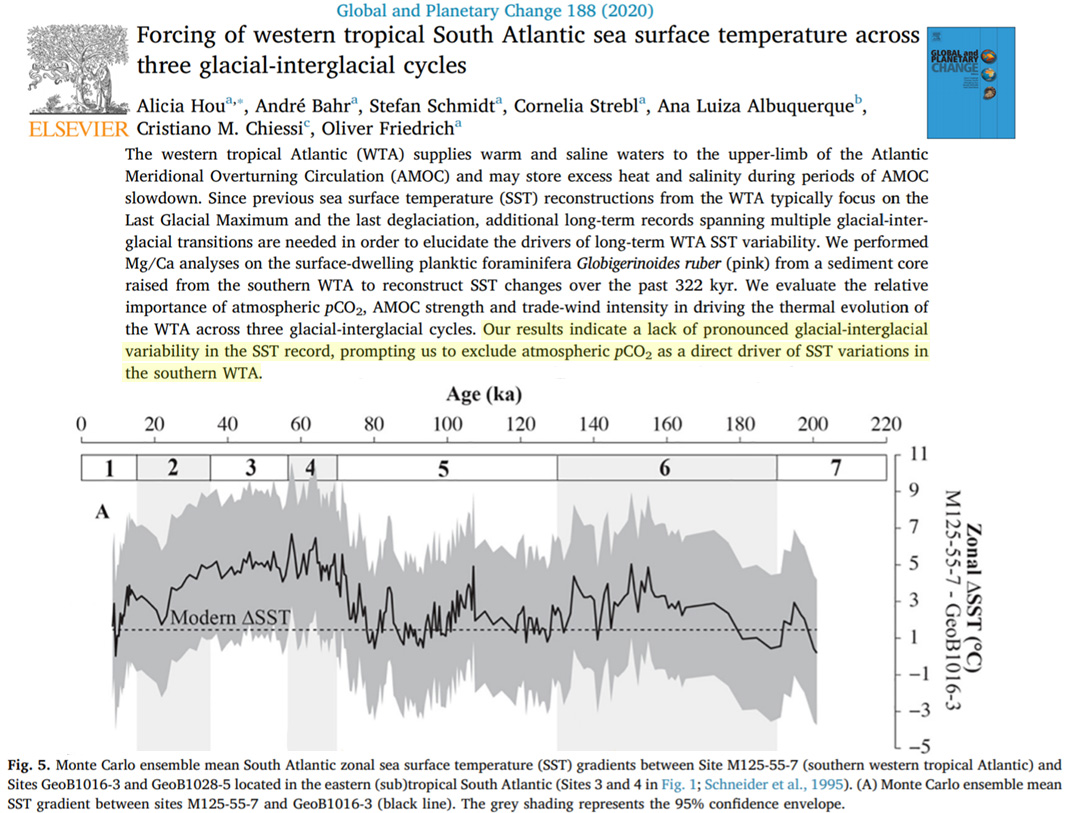
Image Source: Hou et al., 2020
A Southern Ocean site was analyzed in another 2020 study (Ghadi et al.). Sea surface temperatures averaged 1-2°C during glacials and 4°C during interglacials. Today, with a 410 ppm CO2 concentration, this location has again plummeted to glacial/ice age levels (2°C).
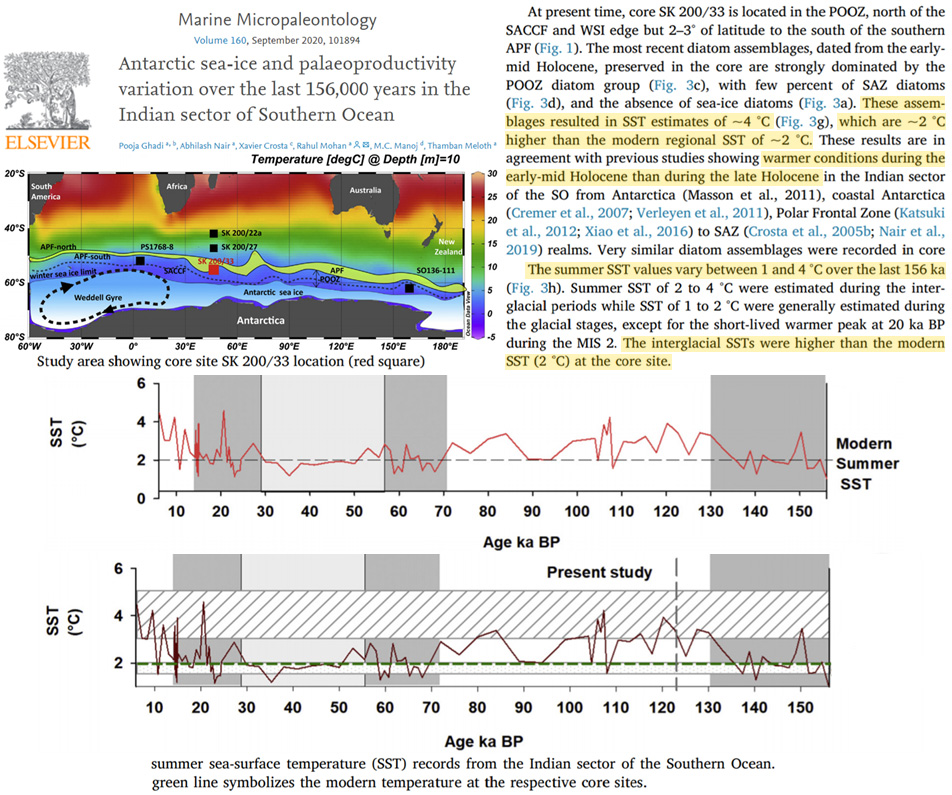
Image Source: Ghadi et al., 2020
The North Atlantic record shows this warmer-during-glacial-periods phenomenon extends to the Northern Hemisphere. The Tobago Basin was “2.5°C warmer than the modern conditions” from 30 to 10 thousand years ago and the Bonaire Basin was 4-6°C warmer than modern from about 20 to 12 thousand years ago (Reißig et al., 2019).
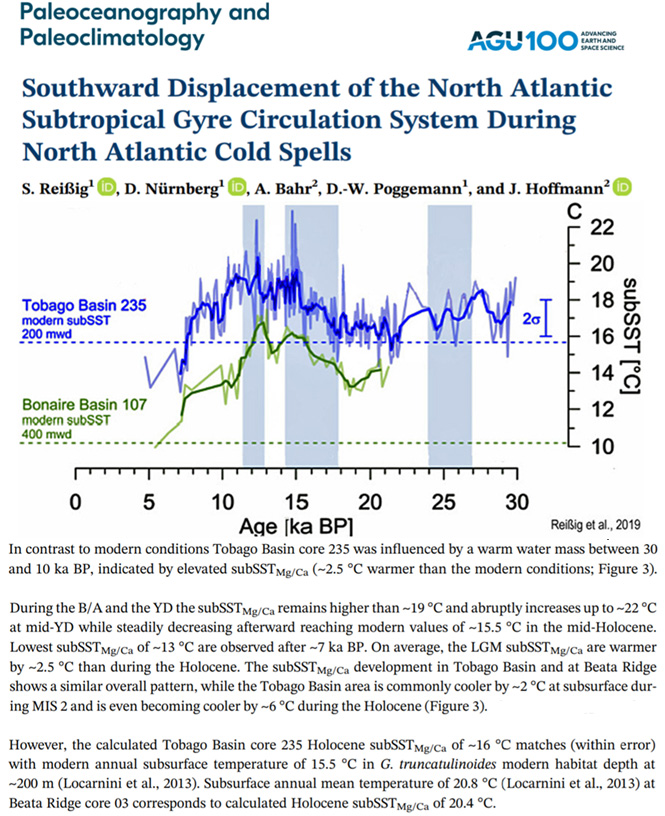
Image Source: Reißig et al., 2019
The warmer-during-glacials phenomenon even extends to the terrestrial landscape. For example, lake temperatures in southern California were 4 to 5°C warmer than today (22 to 23°C versus 18°C) between 30 and 25 thousand years ago (Feakins et al., 2019). Abrupt temperature swings of 10°C occurred in a matter of centuries.
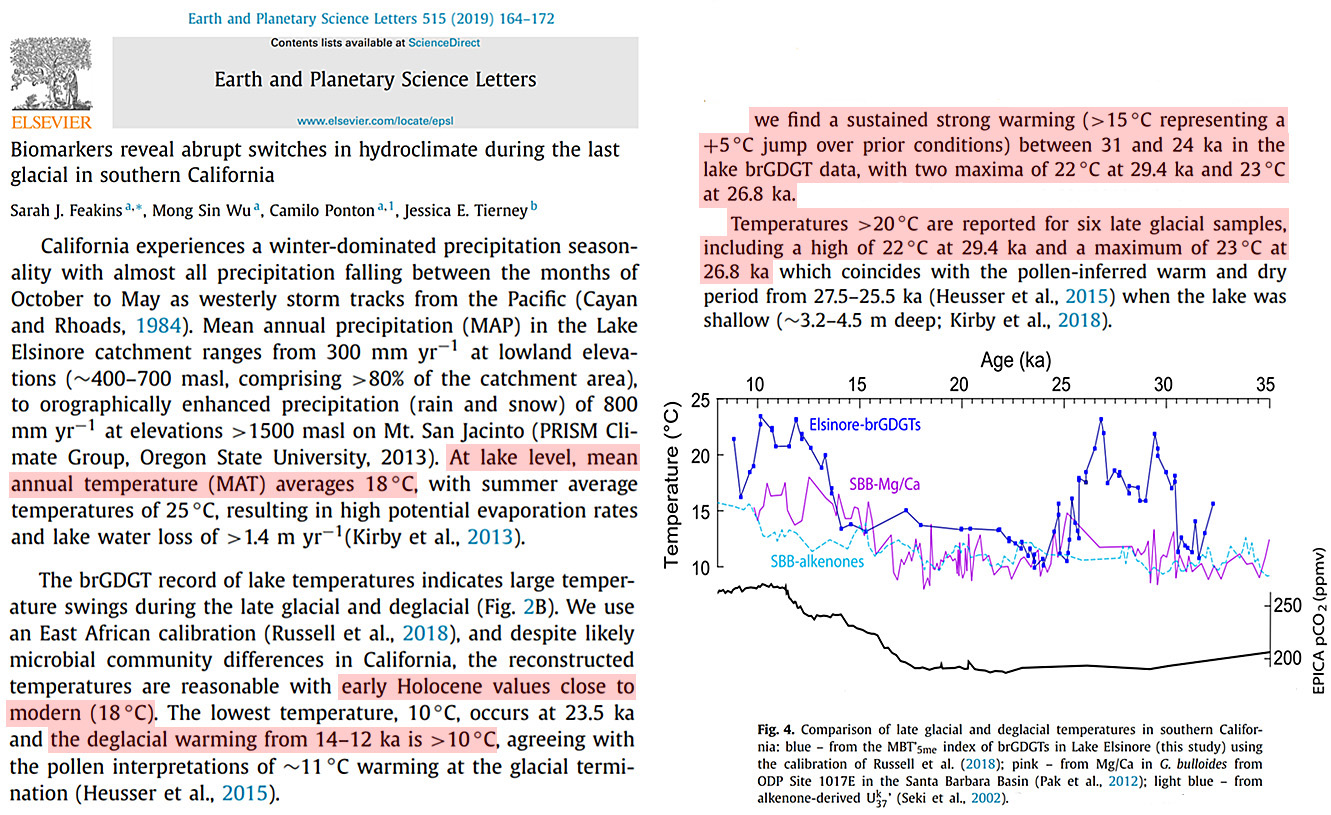
Image Source: Feakins et al., 2019
Even in the high latitudes there was greater warmth during the last glacial period than today. The Russian Altai mountains were “about 3°C warmer than today” 43,000 years ago and up to 5.9°C warmer than now 31,000 years ago (Ganyushkin et al., 2018).
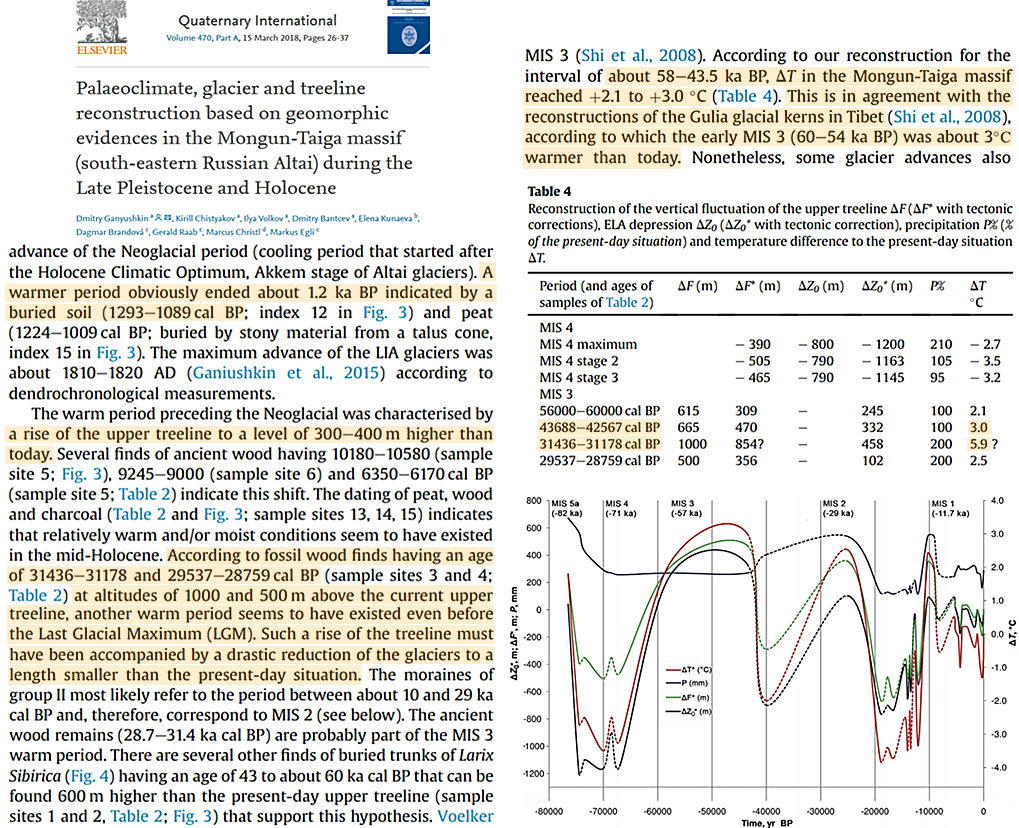
Image Source: Ganyushkin et al., 2018
The North Slope, Alaska (Arctic) temperatures were “higher here than they are today” 20,000 years ago, when wild horses ate grass year-round in this region. As recently as 9 to 8 thousand years ago, the North Slope was still “2 to 3°C warmer than today” (Kuzmina et al., 2019).

Image Source: Kuzmina et al., 2019
There are many more reconstructions appearing in the scientific literature showing modern temperatures are several degrees colder than they were during the last glacial. None of these paleoclimate records support the claim that CO2 concentrations are the “control knob” for Earth’s climate.





Why Go back thousands of years?
Just look at the Central England Temps or even better the Armagh Observatory temps over the last 300 hundred years.
or even three hundred years!
The global average temperature is the result of many factors acting in combination and/or opposition over different time frames.
It is hugely complicated, the atmospheric CO2 concentration is only one of them, not a necessary factor but all else remaining equal a sufficient factor, +1C /doubling of concentration.
A further complication the CO2 concentration can be both cause and effect at the same time.
The current CO2 obsession is a result of the logical fallacy of the single cause:
“… also known as complex cause, causal oversimplification, causal reductionism, and reduction fallacy, is a fallacy of questionable cause that occurs when it is assumed that there is a single, simple cause of an outcome when in reality it may have been caused by a number of only jointly sufficient causes …” (Wiki).
It makes sense that during glacial times if the transport of ocean heat away from the equator, for instance by the AMOC, is reduced, then high latitudes will cool but the tropics either warm or find some other way to lost that heat. Such as cloudiness or thunderstorms. It’s complex indeed – quite right that they challenge simple and complacent assumptions. Not least the one be about CO2.
More absorbed heat by the oceans from solar irradiation due to lower cloudiness induced by lower global tropospheric temperature ?
And then higher SST with respect to the different oceanic pseudo-cycles, when warmer currents get on surface ?
Could it be that during a glacial, oceans can absorb more heat and thousands years later, and that a gradualjy enhanced heat transfer towards the atmosphere somewhat contributes to enter the next inter-glacial ?
A kind of auto-regulated system acting on a large timescale (tens of thousands years) …
Who knows !?
If this is any use to anyone?
https://opentextbc.ca/geology/chapter/16-1-glacial-periods-in-earths-history/
Best wishes for Advent and Christmas… (or Holiday Season.)
[…] Another New Study Determines Sea Surface Temperatures Were 1-5°C Warmer Than Now During The Last IC… […]